Suggest an alkene that, in two steps, could be converted into each of the following ketones. Each sequence should involve a pinacol rearrangement.
(c)
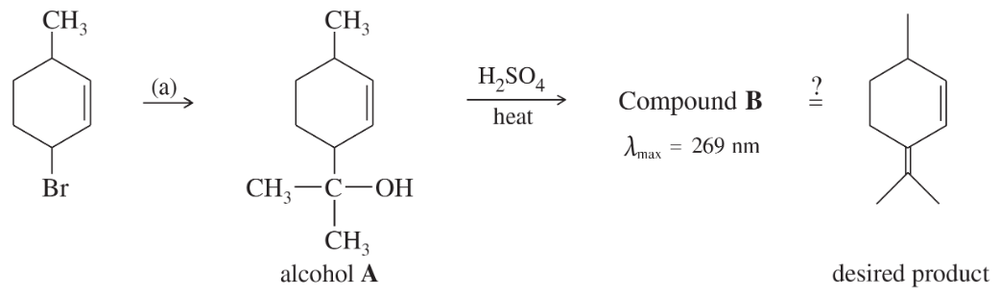
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: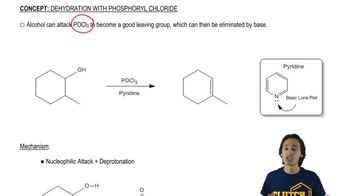



 6:01m
6:01mMaster General features of acid-catalyzed dehydration. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning