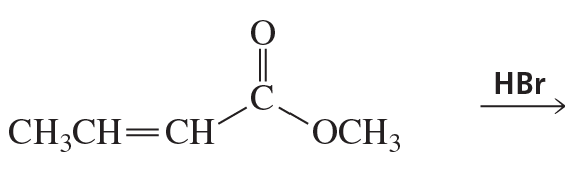
Textbook Question
Propose a mechanism for the conjugate addition of a nucleophile (Nuc:–) to acrylonitrile (H2C=CHCN) and to nitroethylene. Use resonance forms to show how the cyano and nitro groups activate the double bond toward conjugate addition.
423
views