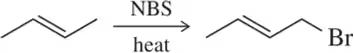The light-initiated reaction of 2,3-dimethylbut-2-ene with N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) gives two products:
b. The bromination of cyclohexene using NBS gives only one major product, as shown on the previous page. Explain why there is no second product from an allylic shift.