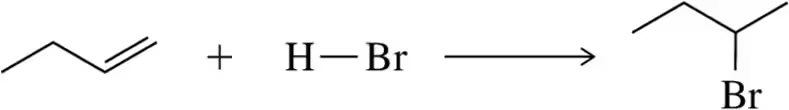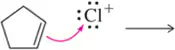Back
BackProblem 1b(i)
(i) Using bond dissociation energies, calculate ∆H° for the following reactions. [BDE for O―H = 110 kcal /mol.]
(b)
Problem 2
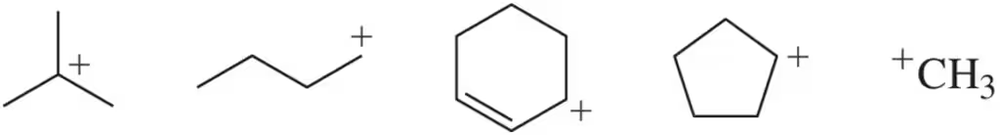
(a) Rank the following carbocations from least stable to most stable. (b) Which would you expect to form first? (c) Which would you expect to react most quickly with a bromide ion (Br⁻) ? [Carbocations, like radicals, are electron deficient.]
Problem 3
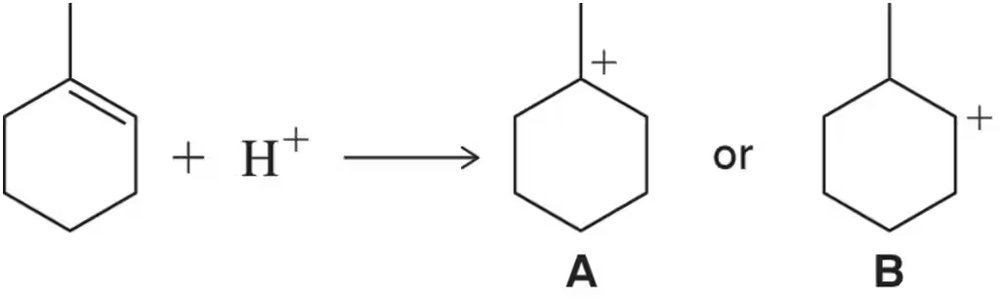
Given that A is more stable than B, draw a reaction coordinate diagram that rationalizes the fact that A forms more quickly than B in the following reaction.
Problem 4
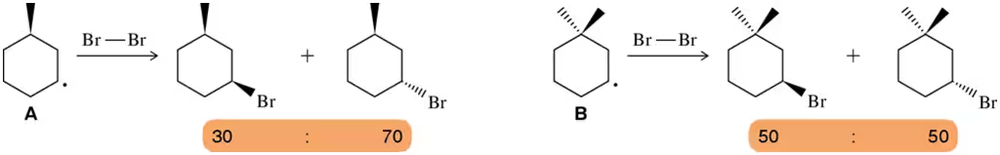
Rationalize the fact that reaction A results in an unequal mixture of products, but reaction B yields an equal mixture of two products.
Problem 5a
Predict the product that results from the following 'pushed electrons.'
(a)
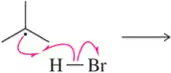
Problem 5c
Predict the product that results from the following 'pushed electrons.'
(c)
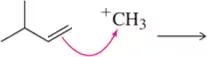
Problem 5f
Predict the product that results from the following 'pushed electrons.'
(f)
Problem 5i
Predict the product that results from the following 'pushed electrons.'
(i)