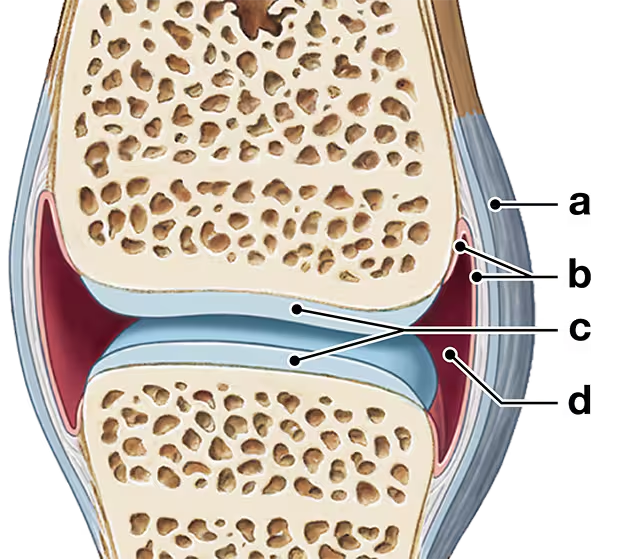
Subacromial, subcoracoid, and subscapular bursae reduce friction in the____joint.
(a) hip
(b) knee
(c) elbow
(d) shoulder
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 1:19m
1:19mMaster Introduction to Classification of Joints with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning