6. Bones & Skeletal Tissue
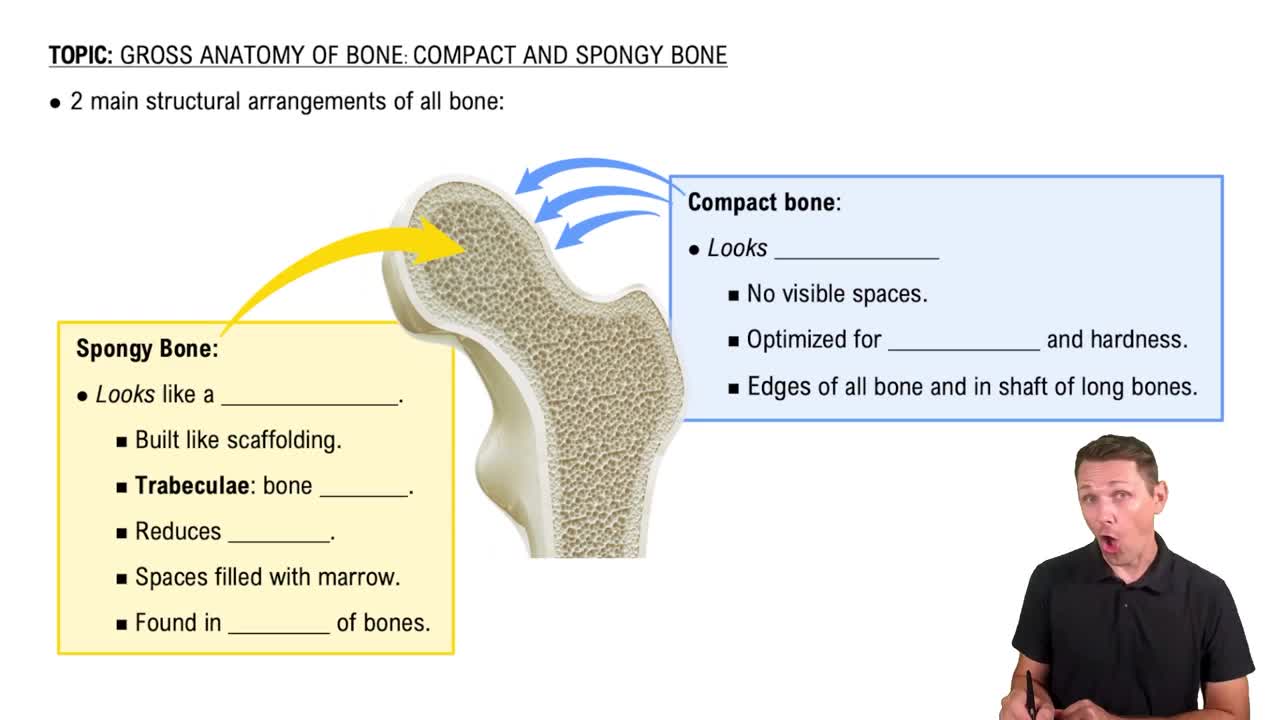
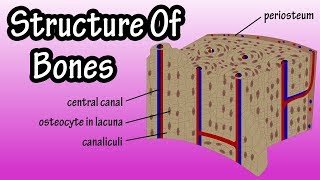
Gross Anatomy of Bone: Compact and Spongy Bone
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following is a canal-like passageway allowing vasculature and nerves to move through the bone?1978views1comments
- Multiple ChoiceBone is broken down by __________.1245views5rank
- Multiple ChoiceThe cells that maintain mature compact bone are __________.2007views3rank
- Multiple ChoiceOsteocytes maintain contact with the blood vessels of the central canal through __________.1792views1rank
- Textbook Question
Correctly order the following steps of bone growth in length by placing a 1 by the first step, a 2 by the second step, and so on.
Calcified cartilage is replaced with bone in the zone of ossification.
Chondrocytes in the zone of proliferation divide by mitosis.
Chondrocytes enter the zone of calcification and die as their matrix calcifies.
Chondrocytes enlarge and cease dividing.
777views2rank - Textbook Question
Yolanda is asked to review a bone slide that her professor has set up under the microscope. She sees concentric layers surrounding a central cavity. Is this bone section taken from the diaphysis or the epiphyseal plate of the specimen?
733views1rank - Textbook Question
What is yellow marrow? How do spongy and compact bone look different?
1026views - Textbook Question
If spongy bone has no osteons, how do nutrients reach the osteocytes?
470views