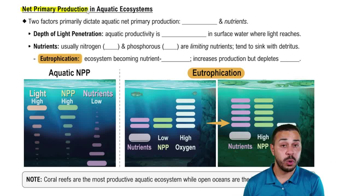
Textbook Question
Birds and mammals are both endothermic, and both have four-chambered hearts. Most reptiles are ectothermic and have three-chambered hearts. Why don't biologists group birds with mammals? Why do most biologists now consider birds to be reptiles?
2005
views