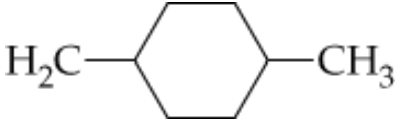
What are the IUPAC names of the following cycloalkanes? Remember to assign priority to the attached groups alphabetically.
b.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 :36m
:36mMaster Rules for Naming Cyclic Alkanes Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning