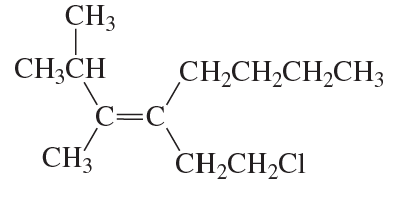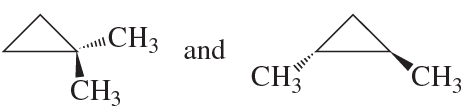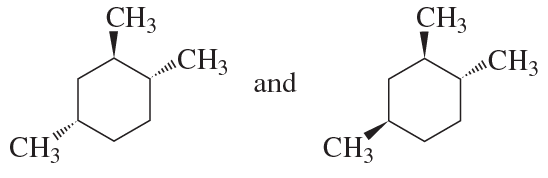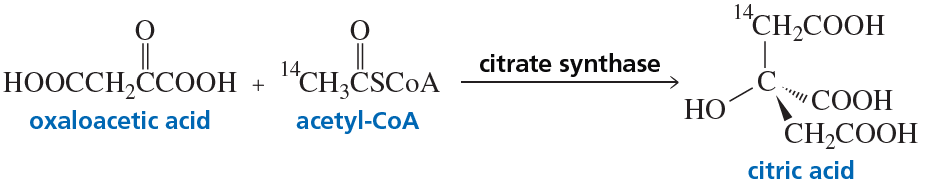Back
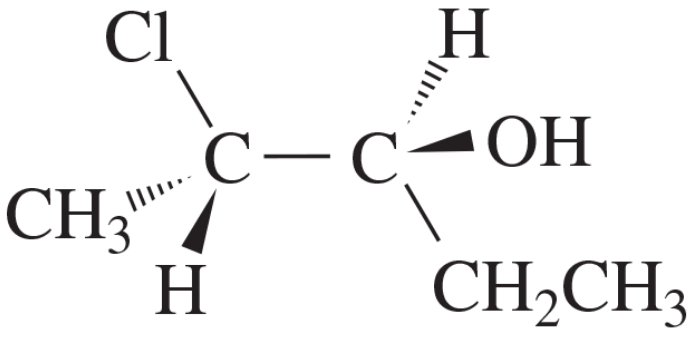
BackProblem 59
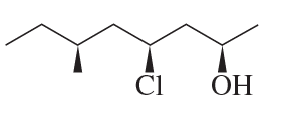
Convert the Fischer projection to a perspective formula.
Problem 61
Convert the perspective formula to a skeletal structure.
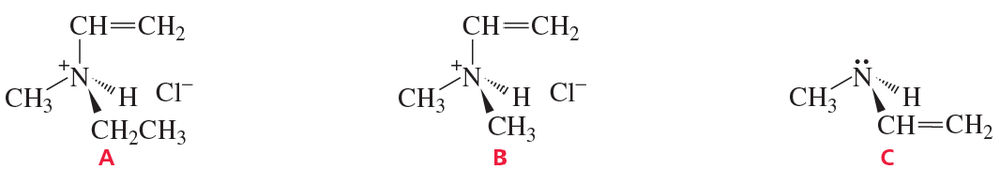
Problem 63
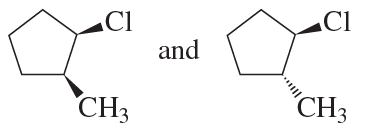
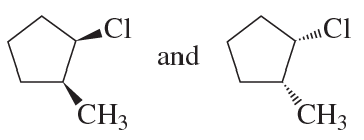
Explain why compound A has two stereoisomers but compounds B and C exist as single compounds.
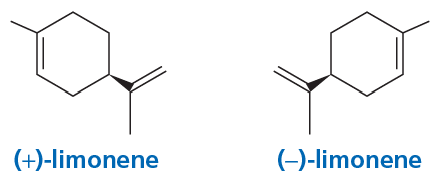
Problem 64
Limonene exists as two different stereoisomers. The R enantiomer is found in oranges and lemons, and the S enantiomer is found in spruce trees. Which of the following is found in oranges and lemons?
Problem 65
Disregarding stereoisomers, draw the structures of all alkenes with molecular formula C5H10. Which ones can exist as cis–trans isomers?
Problem 66a,b
Draw all possible stereoisomers for each of the following. Indicate those compounds for which no stereoisomers are possible.
a. 1-bromo-2-chlorocyclohexane
b. 2-bromo-4-methylpentane
Problem 66c,d
Draw all possible stereoisomers for each of the following. Indicate those compounds for which no stereoisomers are possible.
c. 1,2-dichlorocyclohexane
d. 2-bromo-4-chloropentane
Problem 66e,f
Draw all possible stereoisomers for each of the following. Indicate those compounds for which no stereoisomers are possible.
e. 1-bromo-4-chlorocyclohexane
f. 1,2-dimethylcyclopropane
Problem 67
Which of the following has an asymmetric center?
CHBr2Cl, BHFCl, CH3CHCl2, CHFBrCl, BeHCl
Problem 68c
Name the following compounds using R,S designations:
c.
Problem 70c,d
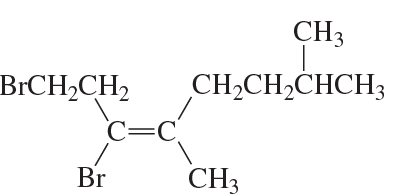
Do the following compounds have the E or the Z configuration?
c.
d.
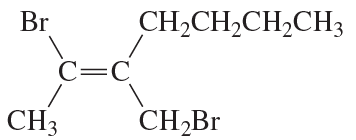
Problem 70e
Do the following compounds have the E or the Z configuration?
e.
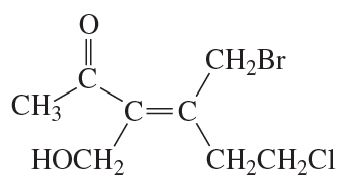
Problem 70f
Do the following compounds have the E or the Z configuration?
f.
Problem 71c,d
Are the following pairs identical, enantiomers, diastereomers, or constitutional isomers?
c.
d.
Problem 71e,f
Are the following pairs identical, enantiomers, diastereomers, or constitutional isomers?
e.
f.
Problem 72c
Assign relative priorities to each set of substituents:
c. -C(=O)CH3, -CH=CH2, -Cl, -C=N
Problem 73a,b
Draw the structure for a compound with molecular formula C2H2I2F2
a. that is optically inactive because it does not have an asymmetric center.
b. that is optically inactive because it is a meso compound.
Problem 73c
Draw the structure for a compound with molecular formula C2H2I2F2
c. that is optically active.
Problem 74
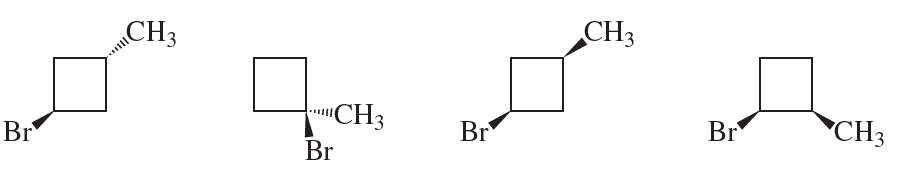
Which of the following are optically active?
Problem 75
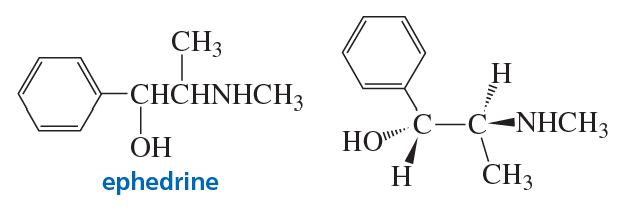
For many centuries, the Chinese have used extracts from a group of herbs known as ephedra to treat asthma. A compound named ephedrine has been isolated from these herbs and found to be a potent dilator of air passages in the lungs.
a. How many stereoisomers does ephedrine have?
b. The stereoisomer shown here is the one that is pharmacologically active. What is the configuration of each of the asymmetric centers?
Problem 76c
Name the following:
c.
Problem 77a,b
Which of the following has an achiral stereoisomer?
a. 2,3-dichlorobutane
b. 2,3-dichloropentane
Problem 77e,f
Which of the following has an achiral stereoisomer?
e. 1,3-dibromocyclobutane
f. 2,4-dibromopentane
Problem 77i,j
Which of the following has an achiral stereoisomer?
i. 1,2-dimethylcyclopentane
j, 1,2-dimethylcyclobutane
Problem 79a,b
Are the following pairs identical, enantiomers, diastereomers, or constitutional isomers?
a.
b.
Problem 80a
Citrate synthase, one of the enzymes in the series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions known as the citric acid cycle, catalyzes the synthesis of citric acid from oxaloacetic acid and acetyl-CoA. If the synthesis is carried out with acetyl-CoA that contains radioactive carbon (14C) in the indicated position, the isomer shown here is obtained.
a. Which stereoisomer of citric acid is synthesized: R or S?
Problem 80b
Citrate synthase, one of the enzymes in the series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions known as the citric acid cycle, catalyzes the synthesis of citric acid from oxaloacetic acid and acetyl-CoA. If the synthesis is carried out with acetyl-CoA that contains radioactive carbon (14C) in the indicated position, the isomer shown here is obtained.
b. If the acetyl-CoA used in the synthesis contains 12C instead of 14C, will the product of the reaction be chiral or achiral?
Problem 81
A solution of an unknown compound (3.0 g of the compound in 200 mL of solution), when placed in a polarimeter tube 2.0 dm long, was found to rotate the plane of polarized light 18° in a counterclockwise direction. What is the specific rotation of the compound?
Problem 82c,d
Are the following pairs identical, enantiomers, diastereomers, or constitutional isomers?
c.
d.
Problem 83
The specific rotation of (R)-(+)-glyceraldehyde is +8.7. If the observed specific rotation of a mixture of (R)-glyceraldehyde and (S)-glyceraldehyde is +1.4, what percent of glyceraldehyde is present as the R enantiomer?