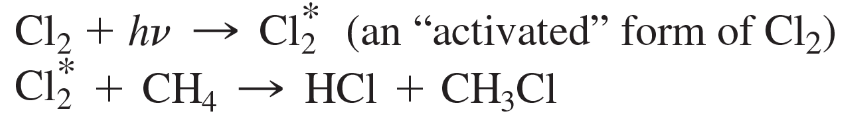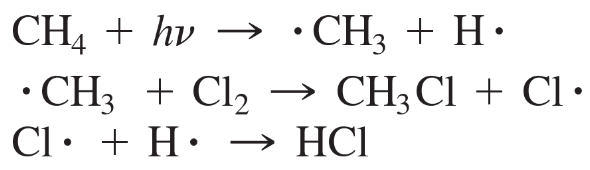Back
BackProblem 1
Draw Lewis structures for the following free radicals.
a. The ethyl radical, CH3—ĊH2
b. The tert-butyl radical, (CH3)3C•
Problem 2a
Write the propagation steps leading to the formation of dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) from chloromethane.
Problem 2b
Explain why free-radical halogenation usually gives mixtures of products.
Problem 2c
How could an industrial plant control the proportions of methane and chlorine to favor production of CCl4? To favor production of CH3Cl?
Problem 3a
Each of the following proposed mechanisms for the free-radical chlorination of methane is wrong. Explain how the experimental evidence disproves each mechanism.
a.
Problem 3b
Each of the following proposed mechanisms for the free-radical chlorination of methane is wrong. Explain how the experimental evidence disproves each mechanism.
b.
- The bromination of methane proceeds through the following steps: 1. Br2 + 2 Br• ΔH° (per mole)/+190 kJ (45 kcal) Ea (per mole)/ 190 kJ (45 kcal) 2. CH4 + Br• —> CH3+ HBr +73 kJ (17 kcal) 79 kJ (19 kcal) 3. • CH3 + Br2 —> CH3Br + Br -112 kJ (-27 kcal) 4 kJ (1 kcal) a. Draw a complete reaction-energy diagram for this reaction. b. Label the rate-limiting step.
Problem 4
- The bromination of methane proceeds through the following steps: 1. Br2 + 2 Br• ΔH° (per mole)/+190 kJ (45 kcal) Ea (per mole)/ 190 kJ (45 kcal) 2. CH4 + Br• —> CH3+ HBr +73 kJ (17 kcal) 79 kJ (19 kcal) 3. • CH3 + Br2 —> CH3Br + Br -112 kJ (-27 kcal) 4 kJ (1 kcal) d. Compute the overall value of ΔH° for the bromination
Problem 4
- Use bond-dissociation enthalpies [TABLE 4-2], p. 167) to calculate values of ΔH° for the following reactions. a. CH3—CH3 + I2 —> CH3CH2I + HI
Problem 4