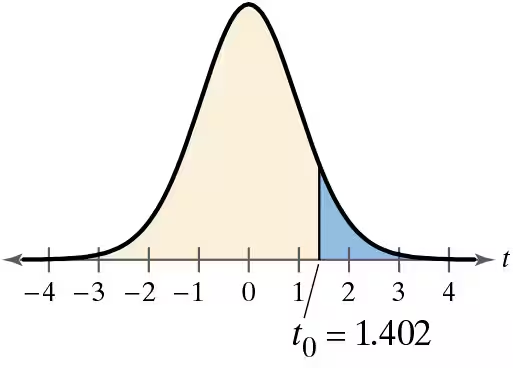
In Exercises 3–8, find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance alpha and sample size n.
Two-tailed test, α=0.05, n=27
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 5:12m
5:12mMaster Intro to Hypothesis Testing with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning