Back
BackProblem 8.RE.6
In Exercises 5– 8, test the claim about the difference between two population means μ1 and μ2 at the level of significance α. Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
Claim: μ1=μ2; α=0.01
Population statistics: σ1= 52 and σ2= 68
Sample statistics: x̅1 = 5595, n1 = 156, and x̅2= 5575, n2= 216
Problem 8.RE.7
In Exercises 5– 8, test the claim about the difference between two population means μ1 and μ2 at the level of significance α. Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
Claim: μ1<μ2; α=0.10
Population statistics: σ1= 0.11 and σ2= 0.10
Sample statistics: x̅1 = 0.28, n1 = 41, and x̅2= 0.33, n2= 34
Problem 8.RE.8
In Exercises 5– 8, test the claim about the difference between two population means μ1 and μ2 at the level of significance α. Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
Claim: μ1≠μ2; α=0.05
Population statistics: σ1= 14 and σ2= 15
Sample statistics: x̅1 = 87, n1 = 410, and x̅2= 85, n2= 340
Problem 8.RE.11
In Exercises 11–16, test the claim about the difference between two population means μ1 and μ2 at the level of significance α. Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
Claim: μ1= μ2; α=0.05. Assume (σ1)^2 = (σ2)^2
Sample statistics: x̅1=228, s1=27, n1= 20 and x̅2=207, s2=25, n2= 13
Problem 8.RE.15
In Exercises 11–16, test the claim about the difference between two population means μ1 and μ2 at the level of significance α. Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
Claim: μ1≠ μ2; α=0.01. Assume (σ1)^2 = (σ2)^2
Sample statistics: x̅1= 61, s1= 3.3, n1= 5 and x̅2= 55.1, s2= 1.2, n2= 7
Problem 8.RE.18a
In Exercises 17 and 18, (a) identify the claim and state Ho and Ha, Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
A real estate agent claims that there is no difference between the mean household incomes of two neighborhoods. The mean income of 12 randomly selected households from the first neighborhood is $52,750 with a standard deviation of $2900. In the second neighborhood, 10 randomly selected households have a mean income of $51,200 with a standard deviation of $2225. At α=0.01, can you reject the real estate agent’s claim? Assume the population variances are equal.
Problem 8.RE.18b
"In Exercises 17 and 18, (b) find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
A real estate agent claims that there is no difference between the mean household incomes of two neighborhoods. The mean income of 12 randomly selected households from the first neighborhood is $52,750 with a standard deviation of $2900. In the second neighborhood, 10 randomly selected households have a mean income of $51,200 with a standard deviation of $2225. At α=0.01, can you reject the real estate agent’s claim? Assume the population variances are equal."
Problem 8.RE.18c
In Exercises 17 and 18, (c) find the standardized test statistic t, Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
A real estate agent claims that there is no difference between the mean household incomes of two neighborhoods. The mean income of 12 randomly selected households from the first neighborhood is $52,750 with a standard deviation of $2900. In the second neighborhood, 10 randomly selected households have a mean income of $51,200 with a standard deviation of $2225. At α=0.01, can you reject the real estate agent’s claim? Assume the population variances are equal.
Problem 8.RE.18e
In Exercises 17 and 18, (e) interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
A real estate agent claims that there is no difference between the mean household incomes of two neighborhoods. The mean income of 12 randomly selected households from the first neighborhood is $52,750 with a standard deviation of $2900. In the second neighborhood, 10 randomly selected households have a mean income of $51,200 with a standard deviation of $2225. At α=0.01, can you reject the real estate agent’s claim? Assume the population variances are equal.
Problem 8.TM.4
In Exercises 4 and 5, use technology to perform a two-sample t-test to determine whether there is a difference in the mint dates and in the values of coins found on a street from 1985 through 1996 for the two mint locations. Write your conclusion as a sentence. Use α = 0.05.
Mint dates of coins (years)
Philadelphia: x̅1=1984.8, s1=8.6
Denver: x̅2=1983.4, s2=8.4
Assume population variances are equal.
Problem 8.T.5
In Exercises 4 and 5, use technology to perform a two-sample t-test to determine whether there is a difference in the mint dates and in the values of coins found on a street from 1985 through 1996 for the two mint locations. Write your conclusion as a sentence. Use α = 0.05.
Value of coins (dollars)
Philadelphia: x̅1=$0.034, s1=$0.054
Denver: x̅2=$0.033, s2=$0.052
Assume population variances are equal.
Problem 8.T.2a
Take this test as you would take a test in class.For each exercise, perform the steps below.
a. Identify the claim and state and
A real estate agency says that the mean home sales price in Olathe, Kansas, is greater than in Rolla, Missouri. The mean home sales price for 39 homes in Olathe is $392,453. Assume the population standard deviation is $224,902. The mean home sales price for 38 homes in Rolla is $285,787. Assume the population standard deviation is $330,578. At α=0.05, is there enough evidence to support the agency’s claim? (Adapted from Realtor.com)
Problem 8.T.2b
Take this test as you would take a test in class.For each exercise, perform the steps below.
b.Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test or a t-test. Explain your reasoning.
A real estate agency says that the mean home sales price in Olathe, Kansas, is greater than in Rolla, Missouri. The mean home sales price for 39 homes in Olathe is $392,453. Assume the population standard deviation is $224,902. The mean home sales price for 38 homes in Rolla is $285,787. Assume the population standard deviation is $330,578. At α=0.05, is there enough evidence to support the agency’s claim? (Adapted from Realtor.com)
Problem 8.T.2c
Take this test as you would take a test in class.For each exercise, perform the steps below.
c.Find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s).
A real estate agency says that the mean home sales price in Olathe, Kansas, is greater than in Rolla, Missouri. The mean home sales price for 39 homes in Olathe is $392,453. Assume the population standard deviation is $224,902. The mean home sales price for 38 homes in Rolla is $285,787. Assume the population standard deviation is $330,578. At α=0.05, is there enough evidence to support the agency’s claim? (Adapted from Realtor.com)
Problem 8.T.2d
Take this test as you would take a test in class.For each exercise, perform the steps below.
d. Find the appropriate standardized test statistic.
A real estate agency says that the mean home sales price in Olathe, Kansas, is greater than in Rolla, Missouri. The mean home sales price for 39 homes in Olathe is $392,453. Assume the population standard deviation is $224,902. The mean home sales price for 38 homes in Rolla is $285,787. Assume the population standard deviation is $330,578. At α=0.05, is there enough evidence to support the agency’s claim? (Adapted from Realtor.com)
Problem 8.T.2e
Take this test as you would take a test in class.For each exercise, perform the steps below.
e. Decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
A real estate agency says that the mean home sales price in Olathe, Kansas, is greater than in Rolla, Missouri. The mean home sales price for 39 homes in Olathe is $392,453. Assume the population standard deviation is $224,902. The mean home sales price for 38 homes in Rolla is $285,787. Assume the population standard deviation is $330,578. At α=0.05, is there enough evidence to support the agency’s claim? (Adapted from Realtor.com)
Problem 8.RE.10
"In Exercises 9 and 10, (a) identify the claim and state Ho and Ha , (b) find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), (c) find the standardized test statistic z, (d) decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and (e) interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
A career counselor claims that the mean annual salaries of entry level paralegals in Dayton, Ohio, and Coventry, Rhode Island, are the same. The mean annual salary of 40 randomly selected entry level paralegals in Dayton is $58,180. Assume the population standard deviation is $10,990. The mean annual salary of 35 randomly selected entry level paralegals in Coventry is $61,120. Assume the population standard deviation is $11,850. At α=0.10, is there enough evidence to reject the counselor’s claim? (Adapted from Salary.com)"
Problem 8.T.2f
"Take this test as you would take a test in class.For each exercise, perform the steps below.
f. Interpret the decision in the context of the original claim.
A real estate agency says that the mean home sales price in Olathe, Kansas, is greater than in Rolla, Missouri. The mean home sales price for 39 homes in Olathe is $392,453. Assume the population standard deviation is $224,902. The mean home sales price for 38 homes in Rolla is $285,787. Assume the population standard deviation is $330,578. At α=0.05, is there enough evidence to support the agency’s claim? (Adapted from Realtor.com) "
Problem 8.1.5
Independent and Dependent Samples In Exercises 5– 8, classify the two samples as independent or dependent and justify your answer.
Sample 1: The maximum bench press weights for 53 football players
Sample 2: The maximum bench press weights for the same 53 football players after completing a weight lifting program
Problem 8.1.2
Explain how to perform a two-sample z-test for the difference between two population means using independent samples with and known.
Problem 8.1.3
Describe another way you can perform a hypothesis test for the difference between the means of two populations using independent samples with and known that does not use rejection regions.
Problem 8.1.8
Independent and Dependent Samples In Exercises 5– 8, classify the two samples as independent or dependent and justify your answer.
Sample 1: The commute times of 10 workers when they use their own vehicles
Sample 2: The commute times of the same 10 workers when they use public transportation
Problem 8.1.13
In Exercises 11 –14, test the claim about the difference between two population means and at the level of significance . Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
Claim: μ1<μ2; α=0.05
Population statistics:σ1=75 and σ2=105
Sample Statistics: x̅1=2435, n1=35, x̅2=2432, n2=90
Problem 8.1.14
In Exercises 11 –14, test the claim about the difference between two population means and at the level of significance . Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
Claim: μ1<μ2; α=0.03
Population statistics:σ1=136 and σ2=215
Sample Statistics: x̅1=5004, n1=144, x̅2=4895, n2=156
Problem 8.1.15
Testing the Difference Between Two Means In Exercises 15–24, (a) identify the claim and state Ho and Ha, (b) find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), (c) find the standardized test statistic z, (d) decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and (e) interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
Braking Distances To compare the dry braking distances from 60 to 0 miles per hour for two makes of automobiles, a safety engineer conducts braking tests for 16 compact SUVs and 11 midsize SUVs. The mean braking distance for the compact SUVs is 131.8 feet. Assume the population standard deviation is 5.5 feet. The mean braking distance for the midsize SUVs is 132.8 feet. Assume the population standard deviation is 6.7 feet. At α=0.10 , can the engineer support the claim that the mean braking distances are different for the two categories of SUVs? (Adapted from Consumer Reports)
Problem 8.1.17
Test the claim about the difference between two population means and at the level of significance α. Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
Claim: μ1=μ2, α=0.01, Assume (σ1)^2=(σ2)^2
Problem 8.1.19
Testing the Difference Between Two Means In Exercises 15–24, (a) identify the claim and state Ho and Ha, (b) find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), (c) find the standardized test statistic z, (d) decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and (e) interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
ACT Mathematics and Science Scores The mean ACT mathematics score for 60 high school students is 20.2. Assume the population standard deviation is 5.7. The mean ACT science score for 75 high school students is 20.6. Assume the population standard deviation is 5.9. At α=0.01, can you reject the claim that ACT mathematics and science scores are equal? (Source: ACT, Inc.)
Problem 8.1.25
Getting at the Concept Explain why the null hypothesis Ho: μ1=μ2 is equivalent to the null hypothesis .Ho: μ1-μ2=0
Problem 8.1.20
Testing the Difference Between Two Means In Exercises 15–24, (a) identify the claim and state Ho and Ha, (b) find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), (c) find the standardized test statistic z, (d) decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and (e) interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
ACT English and Reading Scores The mean ACT English score for 120 high school students is 19.9. Assume the population standard deviation is 7.2. The mean ACT reading score for 150 high school students is 21.2. Assume the population standard deviation is 7.1. At α=0.10, can you support the claim that ACT reading scores are higher than ACT English scores? (Source: ACT, Inc.)
Problem 8.1.27
Testing a Difference Other Than Zero Sometimes a researcher is interested in testing a difference in means other than zero. In Exercises 27 and 28, you will test the difference between two means using a null hypothesis of Ho: μ1-μ2=k, Ho: μ1-μ2>=k or Ho: μ1-μ2<=k . The standardized test statistic is still
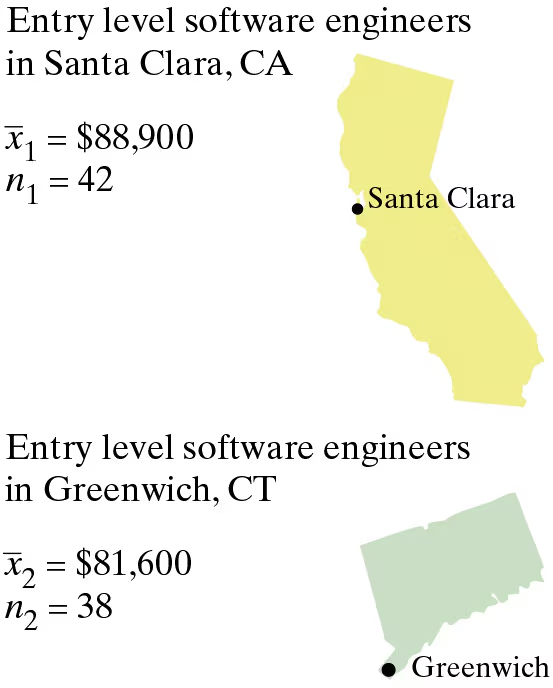
Software Engineer Salaries Is the difference between the mean annual salaries of entry level software engineers in Santa Clara, California, and Greenwich, Connecticut, more than $4000? To decide, you select a random sample of entry level software engineers from each city. The results of each survey are shown in the figure at the left. Assume the population standard deviations are σ1=$14,060 and σ2=$13,050 . At α=0.05, what should you conclude? (Adapted from Salary.com)