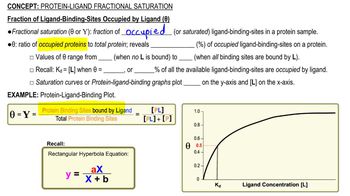
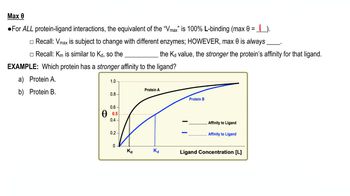
8. Protein Function
Protein-Ligand Fractional Saturation
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Consider the following graph for parts A-C.
A) What is the protein-ligand dissociation constant (Kd) for protein X?
a) 2 µM. b) 4 µM. c) 6 µM. d) 8 µM.
B) What is the protein-ligand dissociation constant (Kd) for protein Y?
a) 2 µM. b) 4 µM. c) 6 µM. d) 8 µM.
C) Which protein has a greater affinity for ligand A?
a) Protein X. b) Protein Y.
456views2rank - Open Question
Match the dissociation constants in the table below to the appropriate curves on the graph.
169views3rank - Multiple Choice
Use the table below to answer questions A, B & C below.
A) Which protein has a greater affinity for their ligand?
B) According to the data in the table, what is the dissociation constant (Kd) for Protein 1?
Protein 1 Kd = ________
C. According to the data in the table, what is the association constant (K a) for Protein 2?
Protein 2 Ka = ________
351views2rank - Multiple Choice
A sample of cells has a total protein-receptor concentration of 10 mM. 25% of the protein-receptors are occupied with ligand when the concentration of free ligand is 15 mM. Calculate the Kd for the receptor-ligand interaction.
205views1rank1comments