Back
BackProblem 1
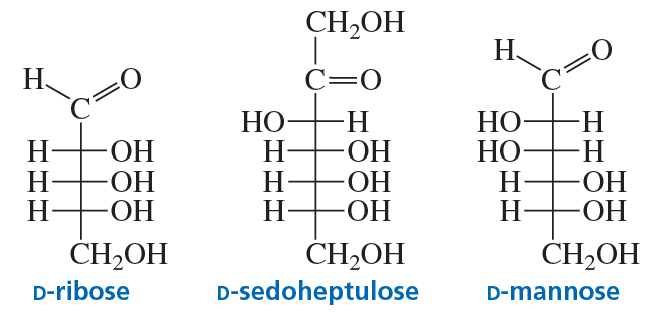
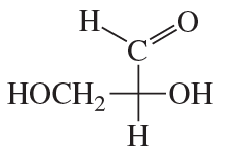
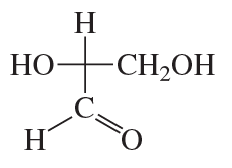
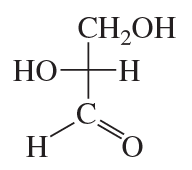
Classify the following monosaccharides:
Problem 2
Draw Fischer projections of L-glucose and L-fructose.
Problem 3
Indicate whether each of the following structures is D-glyceraldehyde or L-glyceraldehyde, assuming that the horizontal bonds point toward you and the vertical bonds point away from you (Section 4.7):
a.
b.
c.
Problem 4
a. Are d-erythrose and l-erythrose enantiomers or diastereomers?
b. Are l-erythrose and l-threose enantiomers or diastereomers?
Problem 5c
c. What sugar is the C-4 epimer of L-gulose?
Problem 5d
d. What sugar is the C-4 epimer of D-lyxose?
Problem 6a
What are the systematic names of the following compounds? Indicate the configuration (R or S) of each asymmetric center.
a. D-glucose
Problem 6b
What are the systematic names of the following compounds? Indicate the configuration (R or S) of each asymmetric center.
b. D-mannose
Problem 7
What sugar is the C-3 epimer of D-fructose?
Problem 8a
How many stereoisomers are possible for a. a ketoheptose?
Problem 8b
How many stereoisomers are possible for b. an aldoheptose?
Problem 11
When D-tagatose is added to a basic aqueous solution, an equilibrium mixture of monosaccharides is obtained, two of which are aldohexoses and two of which are ketohexoses. Identify the aldohexoses and ketohexoses.
Problem 13b
What monosaccharide is reduced to two alditols, one of which is the alditol obtained from the reduction of
1. D-talose?
2. D-allose?
Problem 14a,b
a. Name an aldohexose other than D-glucose that is oxidized to D-glucaric acid by nitric acid.
b. What is another name for D-glucaric acid?
Problem 14c
Name another pair of aldohexoses that are oxidized to identical aldaric acids.
Problem 15a
What monosaccharides are formed in a modified Kiliani–Fischer synthesis starting with each of the following monosaccharides?
a. D-xylose
Problem 16a
What two monosaccharides can be degraded to
a. D-ribose?
Problem 16b
What two monosaccharides can be degraded to
b. D-arabinose?
Problem 19b
4-Hydroxy- and 5-hydroxyaldehydes exist primarily as cyclic hemiacetals. Draw the structure of the cyclic hemiacetal formed by each of the following:
b. 4-hydroxypentanal
Problem 19c
4-Hydroxy- and 5-hydroxyaldehydes exist primarily as cyclic hemiacetals. Draw the structure of the cyclic hemiacetal formed by each of the following:
c. 5-hydroxypentanal
Problem 19d
4-Hydroxy- and 5-hydroxyaldehydes exist primarily as cyclic hemiacetals. Draw the structure of the cyclic hemiacetal formed by each of the following:
d. 4-hydroxyheptanal
Problem 21
D-Glucose most often exists as a pyranose, but it can also exist as a furanose. Draw the Haworth projection of α-D-glucofuranose
Problem 22
Draw the anomers of D-erythrofuranose.
Problem 22-23
When glucose undergoes base-catalyzed isomerization in the absence of the enzyme, mannose is one
of the products that is formed (Section 20.5). Why is mannose not formed in the enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
Problem 24
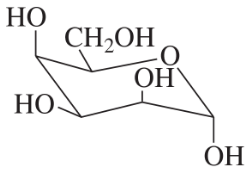
Which OH groups are in the axial position in each of the following?
a. β-D-idopyranose
b. α-D-allopyranose
Problem 25
Draw the products formed when β-D-galactose reacts with ethanol and HCl. (Show all structures as chair conformers.)
Problem 26
Why is only a trace amount of acid used in the formation of an N-glycoside?
Problem 28a
Name the following compounds and indicate whether or not each is a reducing sugar:
a.
Problem 28b
Name the following compounds and indicate whether or not each is a reducing sugar:
b.
Problem 28c
Name the following compounds and indicate whether or not each is a reducing sugar:
c.