Back
BackProblem 29
What is the specific rotation of an equilibrium mixture of fructose? (Hint: Recall that the specific rotation of an equilibrium mixture of glucose is +52.7.)
Problem 30a
a. Identify the sugars in amygdalin.
Problem 30b
b. Identify the glycosidic linkage that connects the sugars.
Problem 31a
What is the main structural difference between a. amylose and cellulose?
Problem 31b
What is the main structural difference between b. amylose and amylopectin?
Problem 31c
What is the main structural difference between c. amylopectin and glycogen?
Problem 31d
What is the main structural difference between d. cellulose and chitin?
Problem 32
Explain why the C-3 OH group of vitamin C is more acidic than the C-2 OH group.
Problem 33a
Refer to Figure 20.5 to answer the following questions: a. People with type O blood can donate blood to anyone, but they cannot receive blood from everyone. From whom can they not receive blood?
Problem 33b
Refer to Figure 20.5 to answer the following questions: b. People with type AB blood can receive blood from anyone, but they cannot give blood to everyone. To whom can they not give blood?
Problem 34b
What product or products are obtained when D-galactose reacts with each of the following?
b. Ag+, NH3, HO-
Problem 34c
What product or products are obtained when D-galactose reacts with each of the following?
c. NaBH4, followed by H3O+
Problem 34d
What product or products are obtained when d-galactose reacts with each of the following?
d. excess CH3I + Ag2O
Problem 34e
What product or products are obtained when D-galactose reacts with each of the following?
e. Br2 in water
Problem 34f
What product or products are obtained when D-galactose reacts with each of the following?
f. ethanol + HCl
Problem 34g
What product or products are obtained when d-galactose reacts with each of the following?
g.
1. hydroxylamine/trace acid
2. acetic anhydride/∆
3. HO-/H2O
Problem 35
Name the epimers of D-glucose.
Problem 36a
Identify the sugar in each description.
a. An aldopentose that is not D-arabinose forms D-arabinitol when it is reduced with NaBH4.
Problem 36b
Identify the sugar in each description.
b. A sugar that is not D-altrose forms D-altraric acid when it is oxidized with nitric acid.
Problem 36c
Identify the sugar in each description.
c. A ketose that, when reduced with NaBH4, forms D-altritol and D-allitol.
Problem 37
D-Xylose and D-lyxose are formed when d-threose undergoes a Kiliani–Fischer synthesis. D-Xylose is oxidized to an optically inactive aldaric acid, whereas D-lyxose forms an optically active aldaric acid. What are the structures of D-xylose and D-lyxose?
Problem 38a,b
Answer the following questions about the eight aldopentoses:
a. Which are enantiomers?
b. Which are C-2 epimers?
Problem 39a
What is the configuration of each of the asymmetric centers in the Fischer projection of
a. D-glucose?
Problem 39b
What is the configuration of each of the asymmetric centers in the Fischer projection of
b. D-galactose?
Problem 39c
What is the configuration of each of the asymmetric centers in the Fischer projection of
c. D-ribose?
Problem 39d
What is the configuration of each of the asymmetric centers in the Fischer projection of
d. D-xylose?
Problem 39e
What is the configuration of each of the asymmetric centers in the Fischer projection of
e. D-sorbose?
Problem 41a
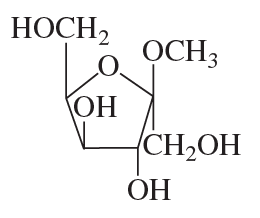
Name the following:
a.
Problem 41b
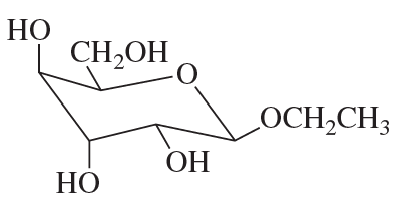
Name the following:
b.
Problem 42
A student isolated a monosaccharide and determined that it had a molecular weight of 150. Much to his surprise, he found that it was not optically active. What is the structure of the monosaccharide?