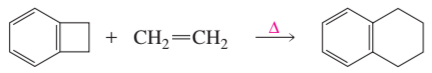Back
BackProblem 23d
Draw the product of each of the following reactions:
d.
Problem 23e
Draw the product of each of the following reactions:
e.
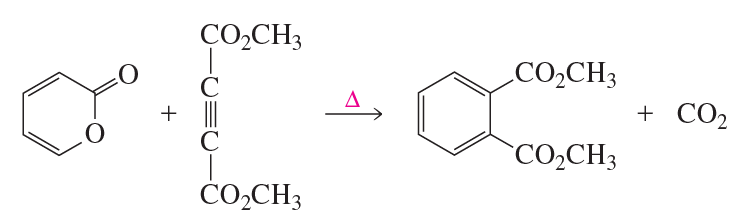
Problem 23f
Draw the product of each of the following reactions:
f.
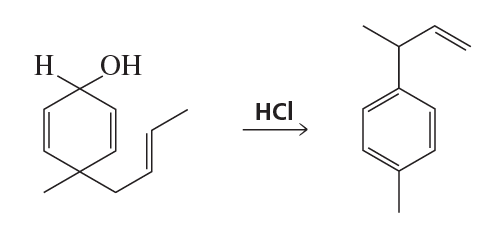
Problem 23g
Draw the product of each of the following reactions:
g.
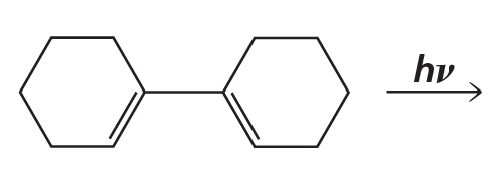
Problem 23h
Draw the product of each of the following reactions:
h.
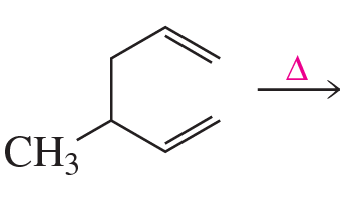
Problem 24c,d
Draw the product of each of the following reactions:
c.
d.
Problem 25
Account for the difference in the products of the following reactions:
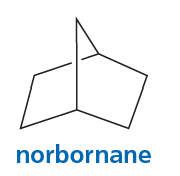
Problem 26
Show how norbornane can be prepared from cyclopentadiene.
Problem 27
Show how the reactant can be converted to the product in two steps.
Problem 28a(1,2)
a. Name the kind of sigmatropic rearrangement that occurs in each of the following reactions.
1.
2.
Problem 28b
Draw the product formed when each of the following compounds undergoes an electrocyclic reaction
b. under photochemical conditions.
1.
2.
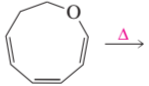
Problem 29d
Draw the product of each of the following reactions:
d.
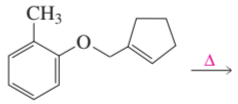
Problem 29e
Draw the product of each of the following reactions:
e.
Problem 32
What is the product of the following [1,3] sigmatropic rearrangement, A or B?
Problem 33
If the compounds shown here are heated, one will form one product from a [1,3] sigmatropic rearrangement and the other will form two products from two different [1,3] sigmatropic rearrangements. Draw the products of the reactions.
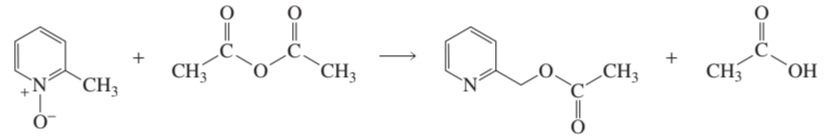
Problem 36
Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:
Problem 37c
Draw the product of each of the following sigmatropic rearrangements:
c.
Problem 37d
Draw the product of each of the following sigmatropic rearrangements:
d.
Problem 38b
b. What would be the product if trans-2-butene were used instead of ethene?
Problem 39
Explain why two different products are formed from disrotatory ring closure of (2E,4Z,6Z)-octatriene, but only one product is formed from disrotatory ring closure of (2E,4Z,6E)-octatriene.
Problem 40
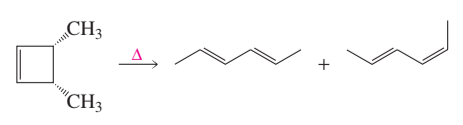
cis-3,4-Dimethylcyclobutene undergoes thermal ring opening to form the two products shown. One of the products is formed in 99% yield, the other in 1% yield. Which is which?
Problem 41
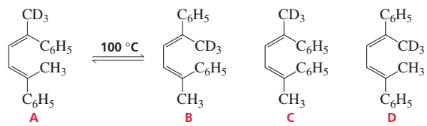
If isomer A is heated to about 100 °C, a mixture of isomers A and B is formed. Explain why there is no trace of isomer C or D.
Problem 42
Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:
Problem 43
Explain why compound A will not undergo a ring-opening reaction under thermal conditions, but compound B will.
Problem 44
A student found that heating any one of the isomers shown here resulted in scrambling of the deuterium to all three positions on the five-membered ring. Propose a mechanism to account for this observation.
Problem 45
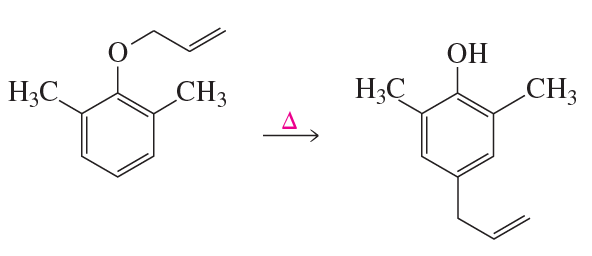
How can this transformation be carried out using only heat or light?
Problem 46
Show the steps involved in the following reaction:
Problem 47
Propose a mechanism for the reaction shown below:












![Chemical structure showing a [1,3] sigmatropic rearrangement with products labeled A and B.](https://static.studychannel.pearsonprd.tech/courses/organic-chemistry/thumbnails/7d32594d-bf7d-4007-b4a3-ad32290b6c43)
![Two chemical structures illustrating [1,3] sigmatropic rearrangements with labeled substituents and bonds.](https://static.studychannel.pearsonprd.tech/courses/organic-chemistry/thumbnails/680a2367-86d3-4ef3-8671-0b5b26018841)
![Chemical structure illustrating a [5,5] sigmatropic rearrangement with a phenyl group and a diene.](https://static.studychannel.pearsonprd.tech/courses/organic-chemistry/thumbnails/30886d49-6415-4309-97db-2ac92f18960f)
![Chemical structure illustrating a [5,5] sigmatropic rearrangement with a benzene ring and a carbon chain.](https://static.studychannel.pearsonprd.tech/courses/organic-chemistry/thumbnails/854fe803-2923-471a-8931-7b3cc94bcf04)