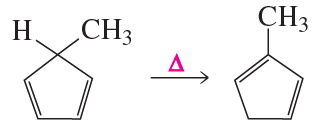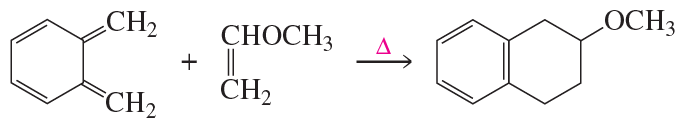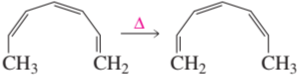Back
BackProblem 1
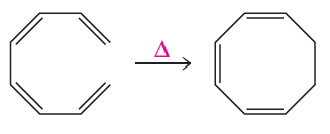
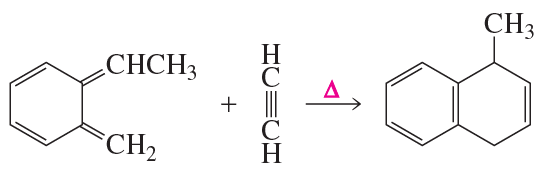
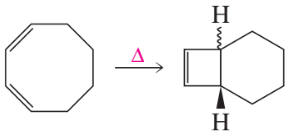
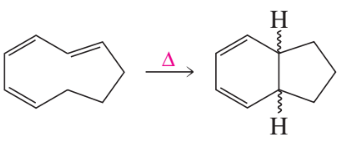
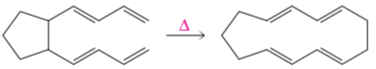
Examine the following pericyclic reactions. For each reaction, tell whether it is an electrocyclic reaction, a cycloaddition reaction, or a sigmatropic rearrangement.
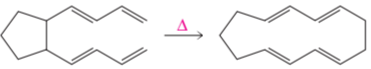
a.
b.
c.
d.
Problem 3
a. How many MOs does 1,3,5,7-octatetraene have?
b. What is the designation of its HOMO (c1, c2, etc.)?
c. How many nodes does its highest energy MO have between the nuclei?
Problem 5
a. For conjugated systems with two, three, four, five, six, and seven conjugated p-bonds, construct quick MOs (just draw the lobes at the ends of the conjugated system as they are drawn on pages 1220 and 1221) to show whether the HOMO is symmetric or antisymmetric.
b. Using these drawings, convince yourself that the Woodward–Hoffmann rules in Table 28.1 are valid.
Problem 6a,b
a. Under thermal conditions, will ring closure of (2E,4Z,6Z,8E)-2,4,6,8-decatetraene be conrotatory or disrotatory?
b. Will the product have the cis or the trans configuration?
Problem 6c,d
c. Under photochemical conditions, will ring closure be conrotatory or disrotatory?
d. Will the product have the cis or the trans configuration?
Problem 7a
Which of the following are correct? Correct any false statements.
a. A conjugated diene with an even number of double bonds undergoes conrotatory ring closure under thermal conditions.
Problem 7b
Which of the following are correct? Correct any false statements.
b. A conjugated diene with an antisymmetric HOMO undergoes conrotatory ring closure under thermal conditions.
Problem 7c
Which of the following are correct? Correct any false statements
c. A conjugated diene with an odd number of double bonds has a symmetric HOMO.
Problem 8a(1)
a. Identify the mode of ring closure for each of the following electrocyclic reactions
1.
Problem 8a(2)
a. Identify the mode of ring closure for each of the following electrocyclic reactions
2.
Problem 8b(2)
b. Are the indicated hydrogens cis or trans?
2.
Problem 8b(1)
b. Are the indicated hydrogens cis or trans?
1.
Problem 9
Compare the reaction between 2,4,6-cycloheptatrienone and cyclopentadiene to the reaction between 2,4,6-cycloheptatrienone and ethene. Why does 2,4,6-cycloheptatrienone use two electrons in one reaction and four electrons in the other?
a.
b.
Problem 10
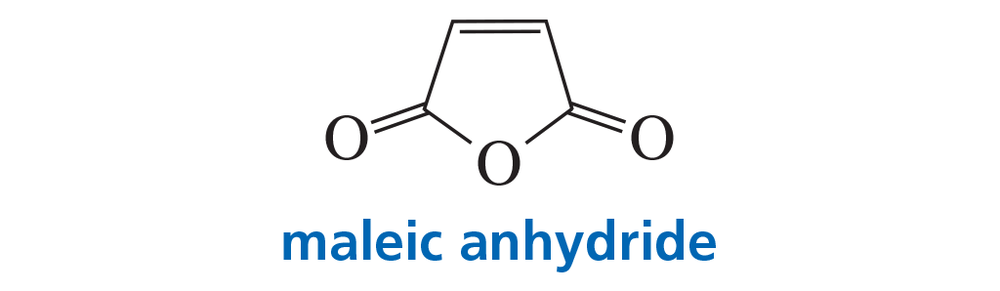
Explain why maleic anhydride reacts rapidly with 1,3-butadiene but does not react at all with ethene under thermal conditions.
Problem 11
Will a concerted reaction take place between 1,3-butadiene and 2-cyclohexenone in the presence of ultraviolet light?
Problem 12a(3)
a. Name the kind of sigmatropic rearrangement that occurs in each of the following reactions.
3.
Problem 12a(4)
a. Name the kind of sigmatropic rearrangement that occurs in each of the following reactions.
4.
Problem 12b(3)
b. Using arrows, show the electron rearrangement that takes place in each reaction.
3.
Problem 12b(4)
b. Using arrows, show the electron rearrangement that takes place in each reaction.
4.
Problem 12b(1,2)
b. Using arrows, show the electron rearrangement that takes place in each reaction.
1.
2.
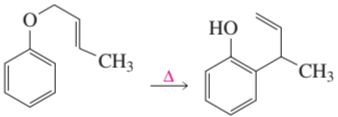
Problem 13b
If the terminal sp2 carbon of the substituent attached to the benzene ring is labeled with 14C, where will the label be in the product?
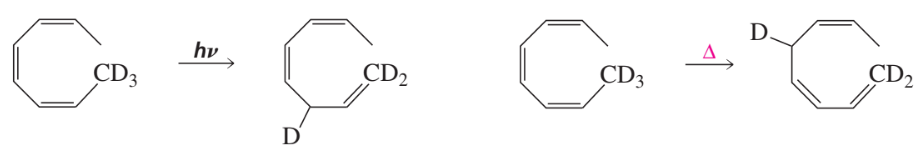
Problem 14
Why was a deuterated compound used in the last reaction on the preceding page?
Problem 15
Account for the difference in the products obtained under photochemical and thermal conditions:
Problem 16
Show how 5-methyl-1,3-cyclopentadiene rearranges to form 1-methyl-1,3-cyclopentadiene and 2-methyl-1,3-cyclopentadiene.
Problem 17
Explain why [1,3] sigmatropic migrations of hydrogen cannot occur under thermal conditions, but [1,3] sigmatropic migrations of carbon can.
Problem 18a
a. Will thermal 1,3-migrations of carbon occur with retention or inversion of configuration?
Problem 18b
b. Will thermal 1,5-migrations of carbon occur with retention or inversion of configuration?
Problem 19
Does the [1,7] sigmatropic rearrangement that converts provitamin D3 to vitamin D3 involve suprafacial or antarafacial rearrangement?
Problem 20
Explain why the hydrogen and the methyl substituent are trans to one another after photochemical ring closure of provitamin D3 to form 7-dehydrocholesterol.
Problem 21
Chorismate mutase is an enzyme that promotes a pericyclic reaction by forcing the substrate to assume the conformation needed for the reaction. The product of the pericyclic reaction is prephenate that is subsequently converted into the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine. What kind of a pericyclic reaction does chorismate mutase catalyze?