Back
BackProblem 19
Draw the important resonance contributors for both resonance-stabilized cations (in brackets) in the mechanism for acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of an amide.
Problem 20a
Propose a mechanism for the hydrolysis of N,N-dimethylacetamide
(a) under basic conditions.
Problem 20b
Propose a mechanism for the hydrolysis of N,N-dimethylacetamide
(b) under acidic conditions.
Problem 20.21
Show how the following ketones might be synthesized from the indicated acids, using any necessary reagents.
(a) propiophenone from propionic acid (using Friedel–Crafts acylation)
Problem 22
Propose a mechanism for the basic hydrolysis of benzonitrile to the benzoate ion and ammonia.
Problem 23
The mechanism for acidic hydrolysis of a nitrile resembles the basic hydrolysis, except that the nitrile is first protonated, activating it toward attack by a weak nucleophile (water). Under acidic conditions, the proton transfer (tautomerism) involves protonation on nitrogen followed by deprotonation on oxygen. Propose a mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of benzonitrile to benzamide.
Problem 24a
In which step(s) of the hydride reduction of an ester does the compound undergo reduction? (Hint: Count the bonds to oxygen.)
Problem 24b
Propose a mechanism for the reduction of octanoyl chloride by lithium aluminum hydride.
Problem 26
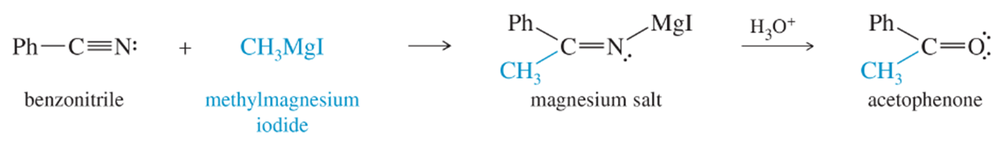
Draw a mechanism for the acidic hydrolysis of the magnesium salt shown below to acetophenone.
Problem 27
Draw a mechanism for the reaction of propanoyl chloride with 2 moles of phenylmagnesium bromide.
Problem 28a
Show how you would add a Grignard reagent to an ester or a nitrile to synthesize
(a) 4-phenylheptan-4-ol.
Problem 28b
Show how you would add a Grignard reagent to an ester or a nitrile to synthesize
(b) heptan-4-ol.
Problem 28c
Show how you would add a Grignard reagent to an ester or a nitrile to synthesize
(c) pentan-2-one.
Problem 30a
Show how Friedel–Crafts acylation might be used to synthesize the following compounds.
a. acetophenone
Problem 30b
Show how Friedel–Crafts acylation might be used to synthesize the following compounds.
b. benzophenone
Problem 30c
Show how Friedel–Crafts acylation might be used to synthesize the following compounds.
c. n-butylbenzene
Problem 32a,b
Show how you would use anhydrides to synthesize the following compounds. In each case, explain why an anhydride might be preferable to an acid chloride.
(a) n-octyl formate
(b) n-octyl acetate
Problem 32c,d
Show how you would use anhydrides to synthesize the following compounds. In each case, explain why an anhydride might be preferable to an acid chloride.
(c) phthalic acid monoamide
(d) succinic acid monomethyl ester
Problem 34a
Suggest the most appropriate reagent for each synthesis, and explain your choice.
(a)
Problem 34b
Suggest the most appropriate reagent for each synthesis, and explain your choice.
(b)
Problem 34c
Suggest the most appropriate reagent for each synthesis, and explain your choice.
(c)
Problem 34d
Suggest the most appropriate reagent for each synthesis, and explain your choice.
(d)
Problem 35a,b,c
Show how you would synthesize each compound, starting with an ester containing no more than eight carbon atoms. Any other necessary reagents may be used.
(a) Ph3C–OH
(b) (PhCH2)2CHOH
(c) PhCONHCH2CH3
Problem 35d,e,f
Show how you would synthesize each compound, starting with an ester containing no more than eight carbon atoms. Any other necessary reagents may be used.
(d) Ph2CHOH
(e) PhCH2OH
(f) PhCOOH
Problem 35i
Show how you would synthesize each compound, starting with an ester containing no more than eight carbon atoms. Any other necessary reagents may be used.
(i) HO–(CH2)8–OH
Problem 36a,b
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic transformations. You may use any necessary reagents.
(a) N-ethylbenzamide → benzylethylamine
(b) ethyl benzoate → N-ethylbenzamide
Problem 36c,d
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic transformations. You may use any necessary reagents.
(c) pyrrolidine → N-acetylpyrrolidine
(d) γ-aminobutyric acid → pyrrolidine
Problem 37
Show how you would accomplish the following syntheses using amides as intermediates. You may use any necessary reagents.
(a) benzoic acid → benzyldimethylamine
(b) pyrrolidine → N-ethylpyrrolidine
(c) cyclopentanecarboxylic acid → cyclopentanecarbonitrile
Problem 38a
Show how you would convert the following starting materials to the indicated nitriles:
(a) phenylacetic acid → phenylacetonitrile
Problem 38b
Show how you would convert the following starting materials to the indicated nitriles:
(b) phenylacetic acid → 3-phenylpropionitrile