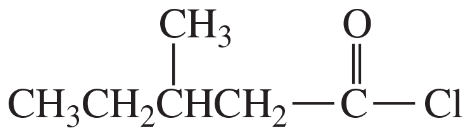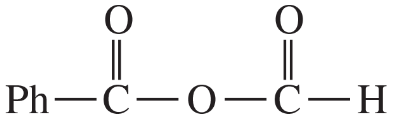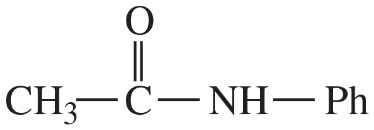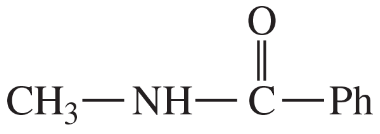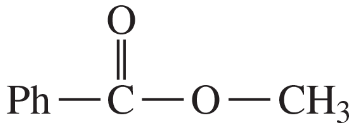Back
BackProblem 38c
Show how you would convert the following starting materials to the indicated nitriles:
(c) p-chloronitrobenzene → p-chlorobenzonitrile
Problem 39a
Show how each transformation may be accomplished by using a nitrile as an intermediate. You may use any necessary reagents.
(a) hexan-1-ol → heptan-1-amine
Problem 39b
Show how each transformation may be accomplished by using a nitrile as an intermediate. You may use any necessary reagents.
(b) cyclohexanecarboxamide → cyclohexyl ethyl ketone
Problem 39c
Show how each transformation may be accomplished by using a nitrile as an intermediate. You may use any necessary reagents.
(c) octan-1-ol → decan-2-one
Problem 40
Propose a mechanism for the reaction of methyl isocyanate with 1-naphthol to give Sevin® insecticide.
Problem 41a,b,c(i)
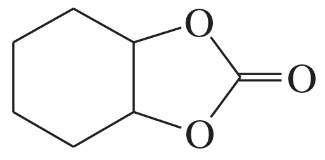
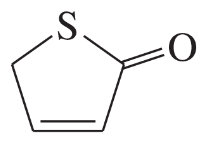
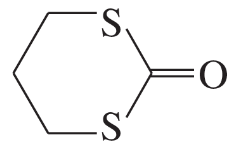
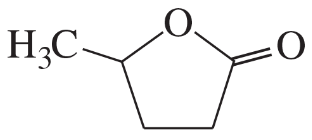
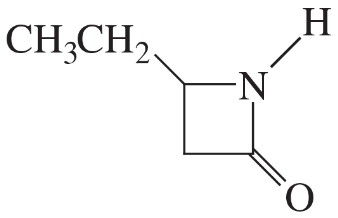
For each heterocyclic compound,
(i) explain what type of acid derivative is present.
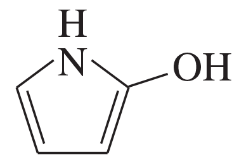
(a)
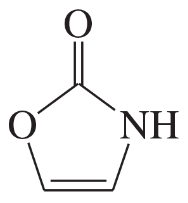
(b)
(c)
Problem 41a,b,c(ii)
For each heterocyclic compound,
(ii) show what compounds would result from complete hydrolysis.
(a)
(b)
(c)
Problem 41a,b,c(iii)
For each heterocyclic compound,
(iii) are any of the rings aromatic? Explain.
(a)
(b)
(c)
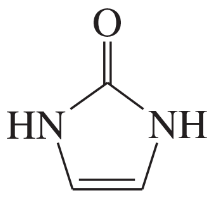
Problem 41d
For each heterocyclic compound,
(i) explain what type of acid derivative is present.
(ii) show what compounds would result from complete hydrolysis.
(iii) are any of the rings aromatic? Explain.
(d)
Problem 41e
For each heterocyclic compound,
(i) explain what type of acid derivative is present.
(ii) show what compounds would result from complete hydrolysis.
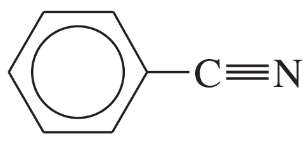
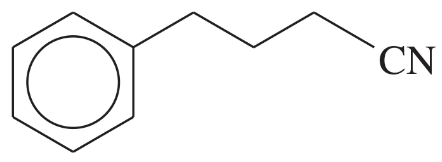
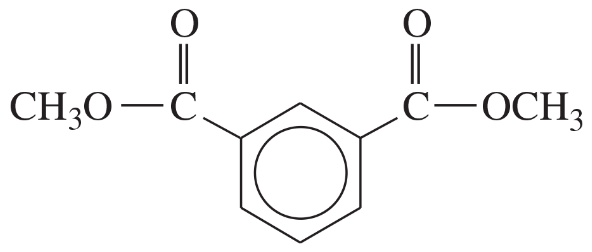
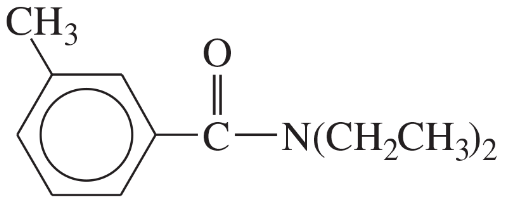
(iii) are any of the rings aromatic? Explain.
(e)
Problem 41f
For each heterocyclic compound,
(i) explain what type of acid derivative is present.
(ii) show what compounds would result from complete hydrolysis.
(iii) are any of the rings aromatic? Explain.
(f)
Problem 42a,b,c
Draw structures to correspond with the following common and systematic names:
(a) phenyl formate
(b) cyclohexyl benzoate
(c) cyclopentyl phenylacetate
Problem 42d,e
Draw structures to correspond with the following common and systematic names:
(d) N-butylacetamide
(e) N,N-dimethylformamide
Problem 42f,g
Draw structures to correspond with the following common and systematic names:
(f) benzoic propionic anhydride
(g) benzamide
Problem 42h
Draw structures to correspond with the following common and systematic names:
(h) γ-hydroxyvaleronitrile
Problem 42k,l
Draw structures to correspond with the following common and systematic names:
(k) phenyl isocyanate
(l) cyclobutyl ethyl carbonate
Problem 42m
Draw structures to correspond with the following common and systematic names:
(m) δ-caprolactam
Problem 42n,o
Draw structures to correspond with the following common and systematic names:
(n) trichloroacetic anhydride
(o) ethyl N-methyl carbamate
Problem 43a,b
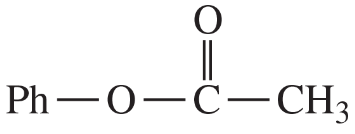
Give appropriate names for the following compounds:
(a)
(b)
Problem 43c,d
Give appropriate names for the following compounds:
(c)
(d)
Problem 43e,f
Give appropriate names for the following compounds:
(e)
(f)
Problem 43g,h
Give appropriate names for the following compounds:
(g)
(h)
Problem 43i,j
Give appropriate names for the following compounds:
(i)
(j)
Problem 43k,l
Give appropriate names for the following compounds:
(k)
(l)
Problem 44a,b,c
Predict the major products formed when benzoyl chloride (PhCOCl) reacts with the following reagents.
(a) ethanol
(b) sodium acetate
(c) aniline
Problem 44d,e,f
Predict the major products formed when benzoyl chloride (PhCOCl) reacts with the following reagents.
(d) anisole and aluminum chloride
(e) excess phenylmagnesium bromide, then dilute acid
(f) LiAlH(O-t-Bu)3
Problem 45a,b,c
Predict the products of the following reactions.
(a) phenol + acetic anhydride
(b) phenol + acetic formic anhydride
(c) aniline + phthalic anhydride
Problem 45d
Predict the products of the following reactions.
(d) anisole + succinic anhydride and aluminum chloride
Problem 45e,f
Predict the products of the following reactions.
(e)
(f)
Problem 46
Acid-catalyzed transesterification and Fischer esterification take place by nearly identical mechanisms. Transesterification can also take place by a base-catalyzed mechanism, but all attempts at base-catalyzed Fischer esterification (using –OR″, for example) seem doomed to failure. Explain why Fischer esterification cannot be catalyzed by base.