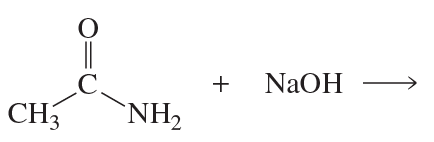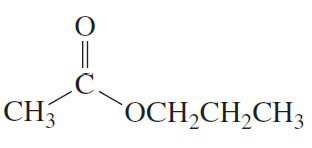Back
Back Bruice 8th Edition
Bruice 8th Edition Ch. 15 - Reactions of Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Ch. 15 - Reactions of Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid DerivativesProblem 2a
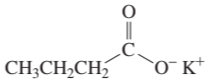
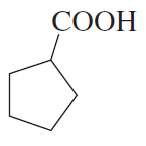
Name the following:
a.
Problem 2c
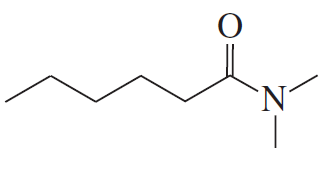
Name the following:
c.
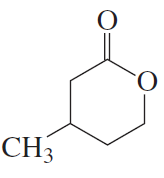
Problem 2e
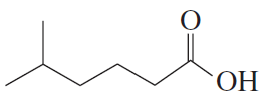
Name the following:
e.
Problem 2g
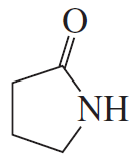
Name the following:
g.
Problem 2h
Name the following:
h.
Problem 2i
Name the following:
i.
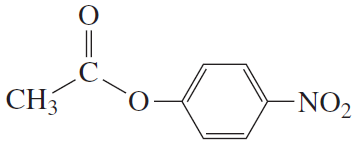
Problem 3a
Draw the structure for each of the following:
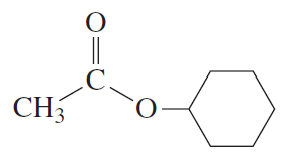
a. phenyl acetate
Problem 3b
Draw the structure for each of the following:
b. γ-caprolactam
Problem 3e
Draw the structure for each of the following:
e. γ-methylcaproic acid
Problem 3f
Draw the structure for each of the following:
f. β-bromobutyramide
Problem 3g
Draw the structure for each of the following:
g. ethyl 2-chloropentanoate
Problem 3h
Draw the structure for each of the following:
h. cyclohexanecarbonyl chloride
Problem 3i
Draw the structure for each of the following:
i. α-chlorovaleric acid
Problem 4
Which is longer, the carbon–oxygen single bond in a carboxylic acid or the carbon–oxygen bond in an alcohol? Why?
Problem 5
There are three carbon–oxygen bonds in methyl acetate.
a. What are their relative bond lengths?
b. What are the relative infrared (IR) stretching frequencies of these bonds?
Problem 6
Which is a correct statement?
A. The delocalization energy of an ester is about 18 kcal/mol, and the delocalization energy of an amide is about 10 kcal/mol.
B. The delocalization energy of an ester is about 10 kcal/mol, and the delocalization energy of an amide is about 18 kcal/mol.
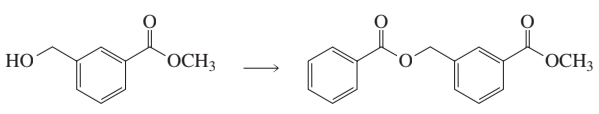
Problem 7
What reagent should be used to carry out the following reaction?
Problem 7b
b. What is the product of the reaction of acetamide with HO−? The pKa of NH3 is 36; the pKa of H2O is 15.7.
Problem 8a
What is the product of an acyl substitution reaction—a new carboxylic acid derivative, a mixture of two carboxylic acid derivatives, or no reaction—if the new group in the tetrahedral intermediate is the following? a. a stronger base than the substituent that is attached to the acyl group
Problem 8b
What is the product of an acyl substitution reaction—a new carboxylic acid derivative, a mixture of two carboxylic acid derivatives, or no reaction—if the new group in the tetrahedral intermediate is the following? b. a weaker base than the substituent that is attached to the acyl group
Problem 10c
Using the pKa values listed in [TABLE 15.1], predict the products of the following reactions:
c.
Problem 10d
Using the pKa values listed in [TABLE 15.1], predict the products of the following reactions:
d.
Problem 12c
Starting with acetyl chloride, what neutral nucleophile would you use to synthesize each of the following compounds?
c.
Problem 12d
Starting with acetyl chloride, what neutral nucleophile would you use to synthesize each of the following compounds?
d.
Problem 12e
Starting with acetyl chloride, what neutral nucleophile would you use to synthesize each of the following compounds?
e.
Problem 12f
Starting with acetyl chloride, what neutral nucleophile would you use to synthesize each of the following compounds?
f.
Problem 13a
Write the mechanism for each of the following reactions:
a. the reaction of acetyl chloride with water to form acetic acid
Problem 13b
Write the mechanism for each of the following reactions:
b. the reaction of benzoyl chloride with excess methylamine to form N-methylbenzamide
Problem 15a
Starting with methyl acetate, what neutral nucleophile would you use to synthesize each of the following compounds? a. ethyl acetate
Problem 15b
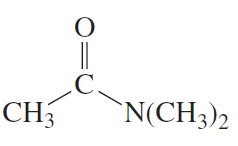
Starting with methyl acetate, what neutral nucleophile would you use to synthesize each of the following compounds? b. acetamide