Back
Back Bruice 8th Edition
Bruice 8th Edition Ch. 15 - Reactions of Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Ch. 15 - Reactions of Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid DerivativesProblem 17a
Write a mechanism for each of the following reactions:
a. the uncatalyzed hydrolysis of methyl propionate.
Problem 17b
Write a mechanism for each of the following reactions:
b. the aminolysis of phenyl formate, using methylamine.
Problem 19a
Which ester hydrolyzes more rapidly? a. methyl acetate or phenyl acetate?
Problem 19b
Which ester hydrolyzes more rapidly? b. phenyl acetate or benzyl acetate?
Problem 21c,d
In the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of an ester,
c. what species is HB+ most likely to be in the hydrolysis reaction?
d. what species is HB+ most likely to be in the reverse reaction?
Problem 22a
Using the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of an ester as your guide, write the mechanism—showing all the curved arrows—for the acid-catalyzed reaction of acetic acid and methanol to form methyl acetate. Use HB+ and :B to represent the proton-donating and proton-removing species, respectively.
Problem 23a,b
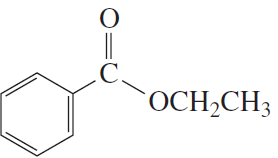
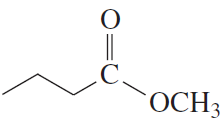
What products are formed from the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of the following esters?
a.
b.
Problem 24
Show the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed formation of 23c starting with the product obtained from its hydrolysis.
Problem 25b
What products are obtained from the following reactions? b. phenyl acetate + excess ethanol + HCl
Problem 26
Write the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed transesterification of ethyl acetate with methanol.
Problem 27
Write the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed reaction of tert-butyl acetate with methanol.
Problem 28b(i)
b. Explain why the rate of aminolysis of an ester cannot be increased by H+.
Problem 28b(ii)
b. Explain why the rate of aminolysis of an ester cannot be increased by HO−, or RO−.
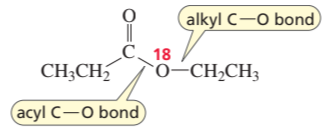
Problem 29
D. N. Kursanov, a Russian chemist, proved that the bond that is broken in the hydroxide-ion-promoted hydrolysis of an ester is the acyl C—O bond, rather than the alkyl C—O bond, by studying the hydrolysis of the following ester under basic conditions:
a. What products contained the 18O label?
b. What product would have contained the 18O label if the alkyl C—O bond had broken?
Problem 31a
Show how each of the following esters could be prepared using a carboxylic acid as one of the starting materials:
a. methyl butyrate (odor of apples)
Problem 32
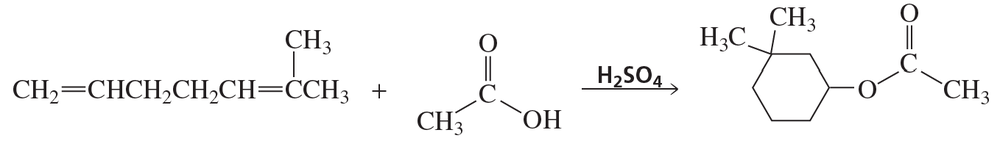
Propose a mechanism for the following reaction. (Hint: Number the carbons to help you see where they end up in the product.)
Problem 33
What acyl chloride and amine are required to synthesize the following amides?
a. N-ethylbutanamide
b. N,N-dimethylbenzamide
Problem 34a
Which of the following reactions lead to the formation of an amide?
Problem 35
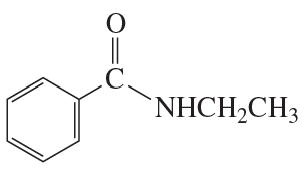
Write the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed reaction of an amide with an alcohol to form an ester.
Problem 36
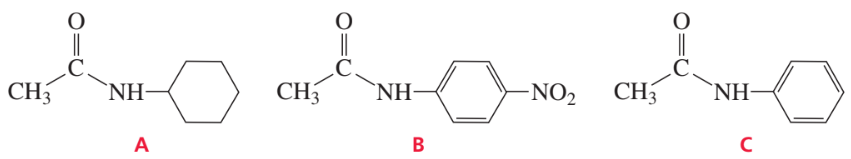
Rank the following amides from greatest reactivity to least reactivity toward acid-catalyzed hydrolysis:
Problem 38a
What alkyl bromide would you use in a Gabriel synthesis to prepare each of the following amines?
a. pentylamine
Problem 38b
What alkyl bromide would you use in a Gabriel synthesis to prepare each of the following amines?
b. isohexylamine
Problem 38c
What alkyl bromide would you use in a Gabriel synthesis to prepare each of the following amines?
c. benzylamine
Problem 38d
What alkyl bromide would you use in a Gabriel synthesis to prepare each of the following amines?
d. cyclohexylamine
Problem 41a,b
Which alkyl halides form the carboxylic acids listed here after reaction with sodium cyanide followed by heating the product in an acidic aqueous solution?
a. butyric acid
b. isovaleric acid
Problem 43a
Propose a mechanism for the reaction of acetic anhydride with water.
Problem 45
We saw that acid anhydrides react with alcohols, water, and amines. In which of these reactions can the tetrahedral intermediate eliminate the carboxylate ion even if it does not lose a proton before the elimination step? Explain.
Problem 46a
Propose a mechanism for the formation of succinic anhydride from succinic acid in the presence of acetic anhydride at neutral pH.
Problem 46b
How does acetic anhydride make it easier to form the anhydride?
Problem 47b
How could you synthesize the following compounds starting with a carboxylic acid?
b.