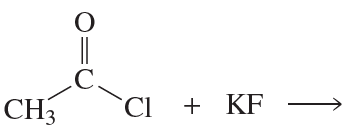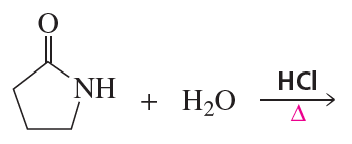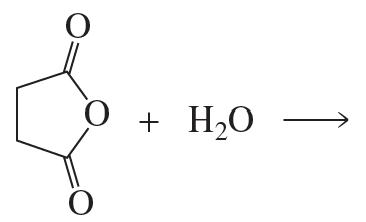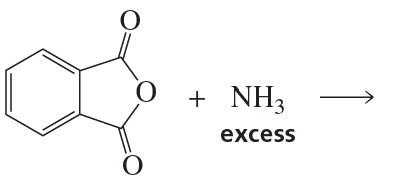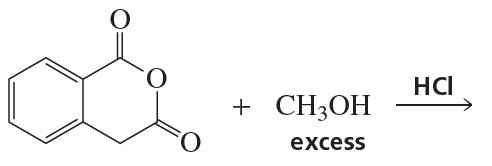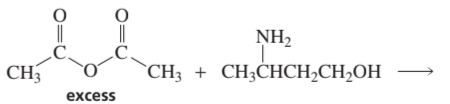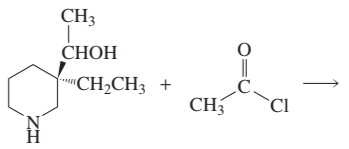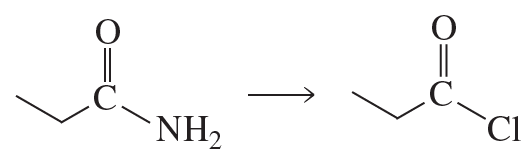Back
Back Bruice 8th Edition
Bruice 8th Edition Ch. 15 - Reactions of Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Ch. 15 - Reactions of Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid DerivativesProblem 63(5)
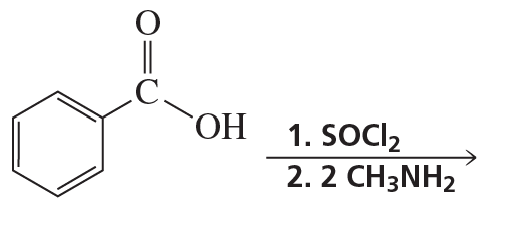
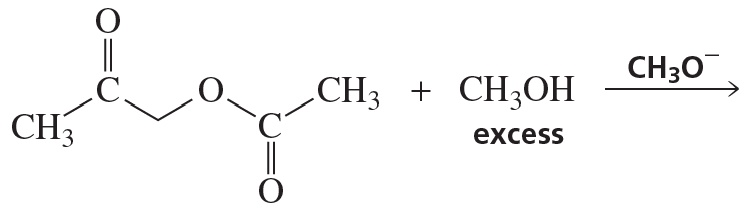
a. Which of the following reactions does not give the carbonyl product shown?
b. Which of the reactions that do not occur can be made to occur if an acid catalyst is added to the reaction mixture?
5.
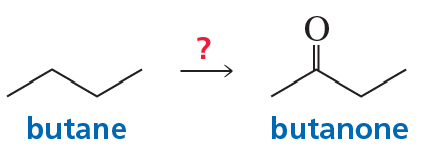
Problem 64
Describe how the target molecule (butanone) can be synthesized in a high yield from butane.
Problem 65
1,4-Diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane (abbreviated DABCO) is a tertiary amine that catalyzes transesterification reactions. Explain how it does this.
Problem 68a,b
What are the products of the following reactions?
a.
b.
Problem 68c
What are the products of the following reactions?
c.
Problem 68d
What are the products of the following reactions?
d.
Problem 68g,h
What are the products of the following reactions?
g.
h.
Problem 68i,j
What are the products of the following reactions?
i.
j.
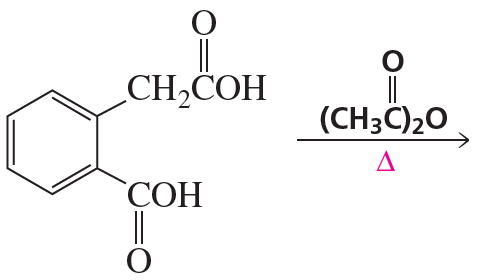
Problem 69c,d
Phosgene (COCl2) was used as a poison gas in World War I. What product would be formed from the reaction of phosgene with each of the following reagents?
c. excess propylamine
d. excess water
Problem 71
When a student treated butanedioic acid with thionyl chloride, she was surprised to find that the product she obtained was an anhydride rather than an acyl chloride. Propose a mechanism to explain why she obtained an anhydride.
Problem 72
When butanoic acid and 18O-labeled methanol react under acidic conditions, what compounds are labeled when the reaction has reached equilibrium?
Problem 74a
a. Identify the two products obtained from the following reaction:
Problem 75
An aqueous solution of a primary or secondary amine reacts with an acyl chloride to form an amide as the major product. However, if the amine is tertiary, an amide is not formed. What product is formed? Explain.
Problem 77a
a. When a carboxylic acid is dissolved in isotopically labeled water (H2O18) and an acid catalyst is added, the label is incorporated into both oxygens of the acid. Propose a mechanism to account for this.
Problem 77a,c
a. When a carboxylic acid is dissolved in isotopically labeled water (H2O18) and an acid catalyst is added, the label is incorporated into both oxygens of the acid. Propose a mechanism to account for this.
c. If an ester is dissolved in isotopically labeled water (H2O18) and an acid catalyst is added, where will the label reside in the product?
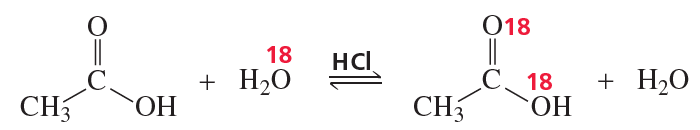
Problem 78
a. A student did not obtain any ester when he added 2,4,6-trimethylbenzoic acid to an acidic solution of ethanol. Why? (HINT: Build models.)
b. Would he have encountered the same problem if he had tried to synthesize the methyl ester of 4-methylbenzoic acid in the same way?
Problem 79
Identify the major and minor products of the following reaction:
Problem 80
When a compound with molecular formula C11H14O2 undergoes acid-catalyzed hydrolysis, one of the products that is isolated gives the following 1H NMR spectrum. Identify the compound.
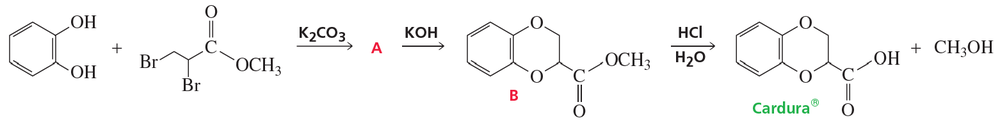
Problem 81a
Cardura, a drug used to treat hypertension, is synthesized as shown here.
a. Identify the intermediate (A) and show the mechanism for its formation.
Problem 81b
Cardura, a drug used to treat hypertension, is synthesized as shown here.
b. Show the mechanism for conversion of A to B. Which is formed more rapidly, A or B?
Problem 82a
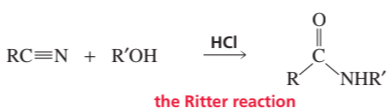
The reaction of a nitrile with an alcohol in the presence of a strong acid forms an N-substituted amide. This reaction, known as the Ritter reaction, does not work with primary alcohols.
a. Propose a mechanism for the Ritter reaction.
Problem 82b
The reaction of a nitrile with an alcohol in the presence of a strong acid forms an N-substituted amide. This reaction, known as the Ritter reaction, does not work with primary alcohols.
b. Why does the Ritter reaction not work with primary alcohols?
Problem 82c
The reaction of a nitrile with an alcohol in the presence of a strong acid forms an N-substituted amide. This reaction, known as the Ritter reaction, does not work with primary alcohols.
c. How does the Ritter reaction differ from the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of a nitrile to form an amide?
Problem 85a
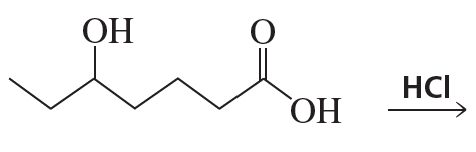
Show how the following compounds could be prepared from the given starting materials. You can use any necessary organic or inorganic reagents.
a.
Problem 85b
Show how the following compounds could be prepared from the given starting materials. You can use any necessary organic or inorganic reagents.
b.
Problem 85c
Show how the following compounds could be prepared from the given starting materials. You can use any necessary organic or inorganic reagents.
c.
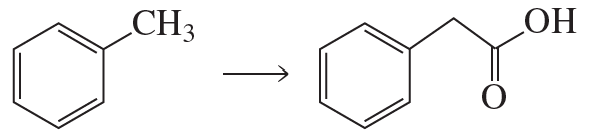
Problem 85d
Show how the following compounds could be prepared from the given starting materials. You can use any necessary organic or inorganic reagents.
d.
Problem 87a
What product do you expect to obtain from each of the following reactions?
a.
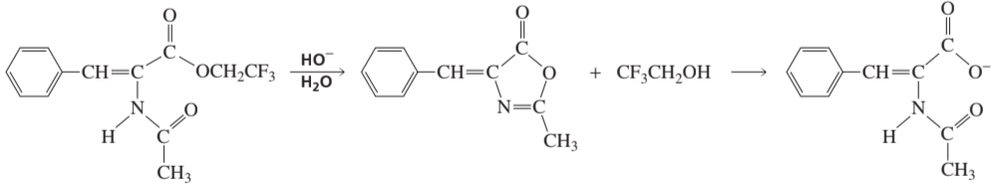
Problem 88
The intermediate shown here is formed during the hydroxide-ion-promoted hydrolysis of the ester group. Propose a mechanism for the reaction.
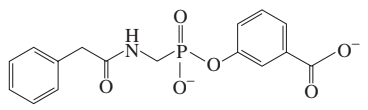
Problem 89a
The following compound has been found to be an inhibitor of penicillinase. The enzyme can be reactivated by hydroxylamine (NH2OH). Propose a mechanism to account for the inhibition.
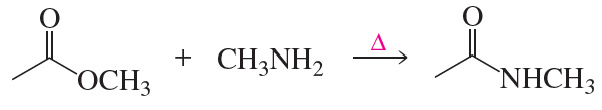
![Chemical structure of 1,4-Diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane (DABCO), a catalyst for transesterification reactions.](https://static.studychannel.pearsonprd.tech/courses/organic-chemistry/thumbnails/c7c3cb11-70de-4a8d-9feb-cf5d5fcb7ded)