Back
BackProblem 1
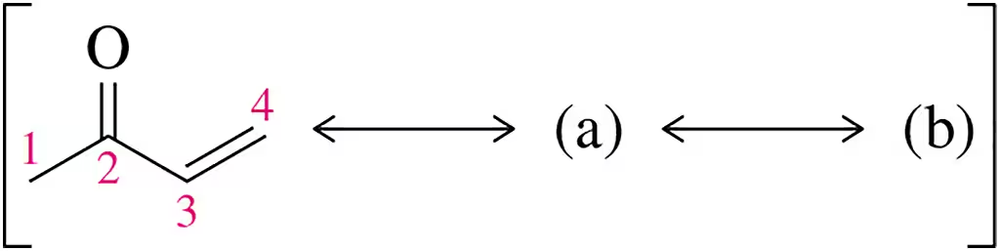
Draw two important resonance structures involving the lone pair on oxygen for the molecule shown. Which carbons are most likely to act as nucleophiles?
Problem 2
Draw two important resonance structures involving the C―O π bond for the molecule shown. To which carbons would you expect a nucleophile to add?
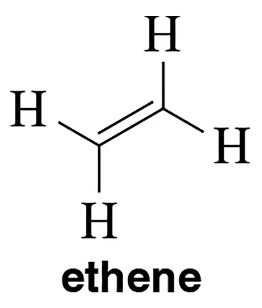
Problem 3a
Draw the molecular orbital picture for (a) ethene. Label the HOMO and LUMO of each.
Problem 4
What frequency of light would be required to excite an electron if the HOMO–LUMO energy gap was 33.9 kcal/mol (142 kJ/mol)?
Problem 5
The SN2 reaction is the concerted, backside displacement of a good leaving group by a nucleophile. Why do nucleophiles attack from the back in SN2 reactions?
Problem 7a
We have studied a number of pericyclic reactions previously. Draw the mechanism of the steps shown. The section number where this material was first studied is given for your review.
(a)
Problem 7b
We have studied a number of pericyclic reactions previously. Draw the mechanism of the steps shown. The section number where this material was first studied is given for your review.
(b)
Problem 7c
We have studied a number of pericyclic reactions previously. Draw the mechanism of the steps shown. The section number where this material was first studied is given for your review.
(c)
Problem 7d
We have studied a number of pericyclic reactions previously. Draw the mechanism of the steps shown. The section number where this material was first studied is given for your review.
(d)
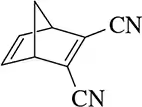
Problem 10
Diene A participates in a fast and efficient Diels–Alder reaction with maleic anhydride, the powerful dienophile from Assessment 22.9. However, the related diene B does not undergo a Diels–Alder reaction. Why?
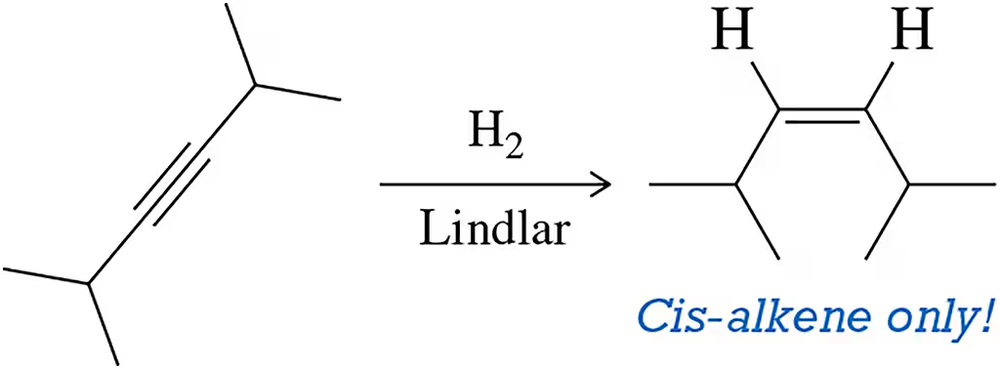
Problem 12
Reduction of an alkyne using the Lindlar catalyst, a reaction presented in Section 10.6.2, produces only the cis-alkene. Why?
Problem 13a
In each Diels–Alder reaction shown, predict the product that will result.
(a)
Problem 13c
In each Diels–Alder reaction shown, predict the product that will result.
(c)
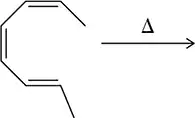
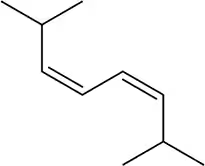
Problem 14
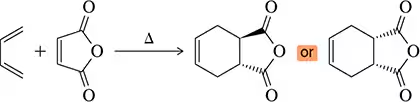
Figure 22.16(a) <IMAGE> shows a unique example where the Diels–Alder reaction gives a single product (no enantiomers) regardless of whether the diene attacks the dienophile from the top or bottom.
(a) Show the product of the diene attacking from the bottom and confirm that the same product is obtained.
(b) What is special about this product that makes this true?
Problem 15c
Assuming the diene approaches the dienophile from the top, predict the product of the following Diels–Alder reactions.
(c)
Problem 18d
Predict the product of the following Diels–Alder reactions. Where a racemic mixture is produced, show both enantiomers and explain how each is formed.
(d)
- In each Diels–Alder reaction shown, predict the product that will result. (a)
Problem 22
Problem 23c
Give the diene and dienophile that could be used to make the following Diels–Alder products.
(c)
Problem 23d
Give the diene and dienophile that could be used to make the following Diels–Alder products.
(d)
Problem 26
What stereochemical result would you expect if the Diels–Alder reaction with the free α,β- unsaturated ketone was faster than reaction with the iminium-bound alkene?
Problem 27a
Predict the product of the following [2 + 2] cycloadditions.
(a)
Problem 27b
Predict the product of the following [2 + 2] cycloadditions.
(b)
Problem 29c
Classify the following conjugated systems as having 4n or 4n + 2 π electrons.
(c)
Problem 30a
Predict the product of the following electrocyclic reactions.
(a)
Problem 30b
Predict the product of the following electrocyclic reactions.
(b)
Problem 30c
Predict the product of the following electrocyclic reactions.
(c)
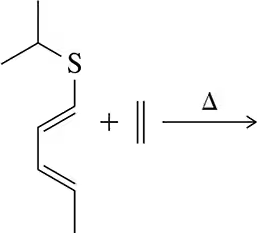
Problem 32b
Predict the product of the following sigmatropic rearrangements. Be sure to rationalize the stereochemical outcome with a chair-like transition state.
(b)
Problem 32d
Predict the product of the following sigmatropic rearrangements. Be sure to rationalize the stereochemical outcome with a chair-like transition state.
(d)
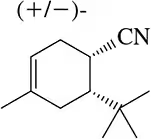
Problem 34c
Identify the following dienes as being in the s-cis or s-trans conformation. If they are in the s-trans conformation, draw them in the s-cis conformation. [It may not always be possible.]
(c)
Problem 34e
Identify the following dienes as being in the s-cis or s-trans conformation. If they are in the s-trans conformation, draw them in the s-cis conformation. [It may not always be possible.]
(e)







![Chemical structures illustrating a [2 + 2] cycloaddition reaction with light energy input indicated.](https://static.studychannel.pearsonprd.tech/courses/organic-chemistry/thumbnails/3f306c3e-e6c5-4df8-b18c-c87ad39b9e61)
![Chemical structure diagram illustrating a [2 + 2] cycloaddition reaction yielding two possible products under light exposure.](https://static.studychannel.pearsonprd.tech/courses/organic-chemistry/thumbnails/a1aef2df-e7dd-4462-9820-3d2aa7482f26)