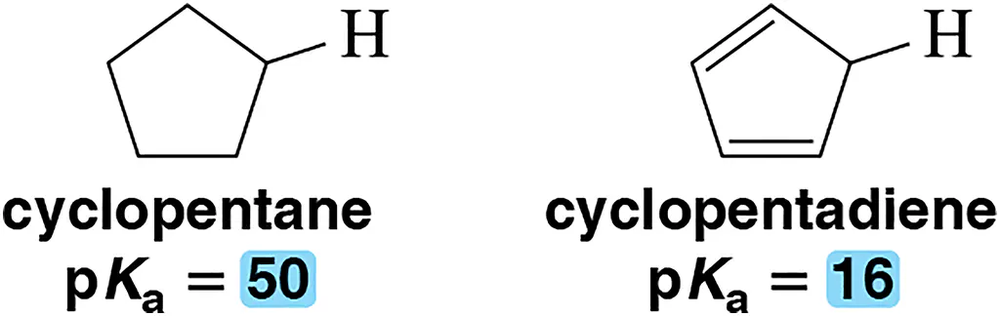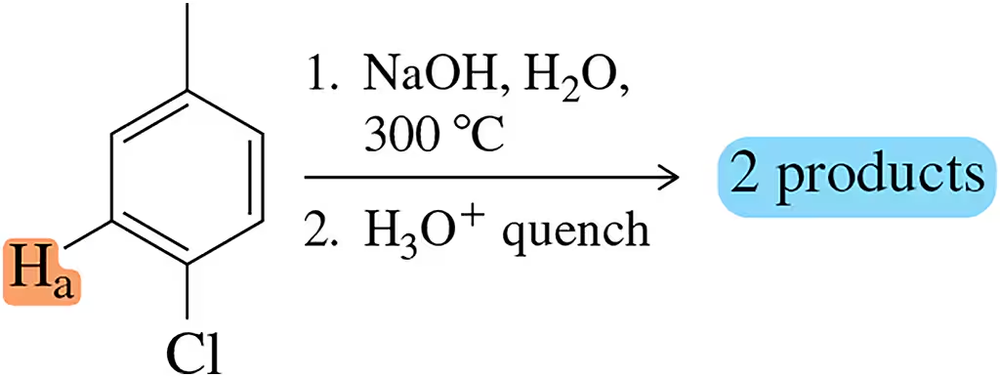Back
BackProblem 2
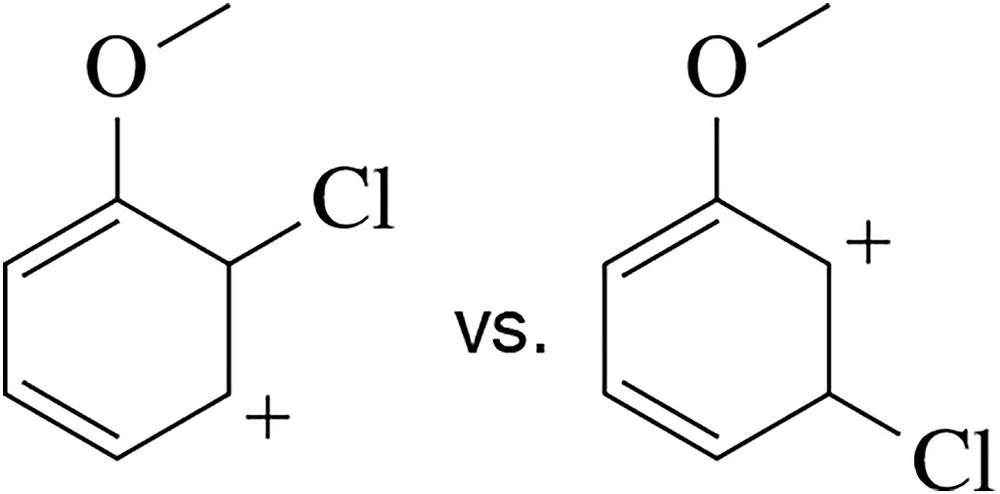
Draw resonance structures to identify which of the following is the more stable carbocation.
Problem 5a
Suggest an arrow-pushing mechanism that accounts for the formation of the following Lewis acid–Lewis base complexes. Label the Lewis acid and Lewis base in each.
(a)
Problem 5b
Suggest an arrow-pushing mechanism that accounts for the formation of the following Lewis acid–Lewis base complexes. Label the Lewis acid and Lewis base in each.
(b)
Problem 7
The average C―C single bond length is 1.53 Å, and the average C=C double bond length is 1.31 Å. All of the C―C bonds in benzene are the same length (1.42 Å). Explain.
Problem 8
If Kekulé's original hypothesis had been correct and benzene was really an equilibrium between two structures, how many distinct isomers would exist for 1,2-dichlorobenzene?
Problem 9
Imidazole is a heteroaromatic base. Which nitrogen, a or b, is most basic?
Problem 10
Between pyrrole and pyrrolidine, which nitrogen would be most nucleophilic? Why?
Problem 12
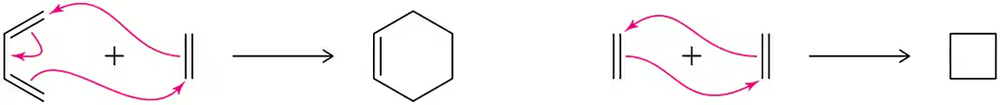
Which of the following concerted reactions would have a more stable transition state? Why?
Problem 13
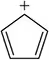
Cyclopentane has pKₐ = 50, whereas cyclopentadiene has pKₐ = 16. Explain this difference.
Problem 14
Which resonance structure, A or B, is most contributing?
Problem 16b
(i) Classify the following molecules as aromatic, nonaromatic, or antiaromatic.
(ii) For the aromatic and antiaromatic molecules, solve for n in Hückel’s/Breslow’s rule. For the other molecules, explain which of the rules of aromaticity is being broken.
(b)
Problem 16d
(i) Classify the following molecules as aromatic, nonaromatic, or antiaromatic.
(ii) For the aromatic and antiaromatic molecules, solve for n in Hückel’s/Breslow’s rule. For the other molecules, explain which of the rules of aromaticity is being broken.
(d)
Problem 21
Draw a Frost circle for the cyclopropenyl anion and compare it to the Frost circle for the cyclopropenyl cation. What has changed?
Problem 22a
Draw a Frost circle for the cyclopentadienyl cation and compare it to the Frost circle for the cyclopentadienyl anion. What has changed?
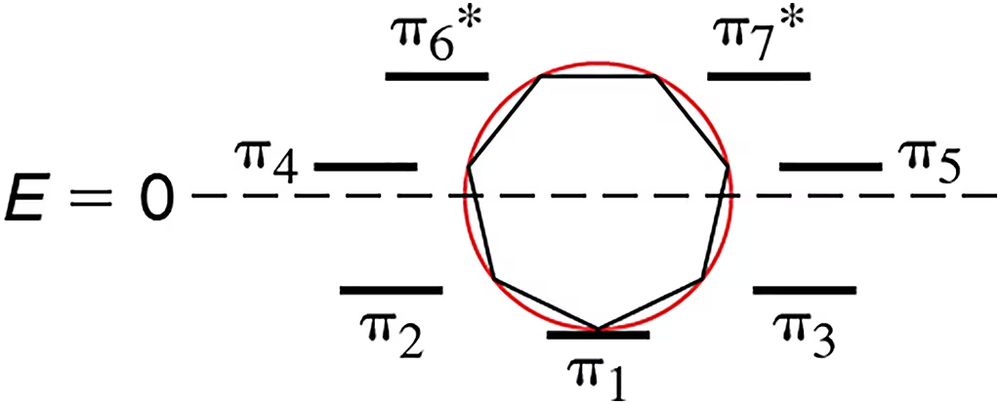
Problem 23
An incomplete Frost diagram for a seven-membered ring is shown. Include the necessary electrons to make it represent an aromatic molecule. Then the draw the structure to which it would correspond.
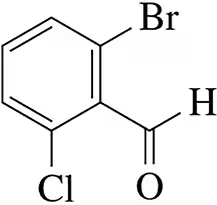
Problem 25c
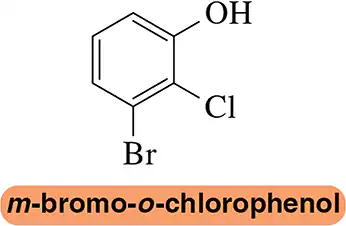
Name the following benzene derivatives according to IUPAC rules.
(c)
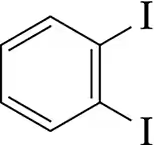
Problem 26a
Name the following benzene derivatives using ortho, meta, and para to identify the relative position of substituents.
(a)
Problem 27b
Convert the given name into the corresponding IUPAC name.
(b)
Problem 29
The zwitterionic form of carbonyls is often used to explain their electrophilicity. Draw the zwitterionic structure of NO+2. Why is this such a great electrophile at the central nitrogen?
Problem 29f
Classify the following conjugated systems as having 4n or 4n + 2 π electrons.
(f)
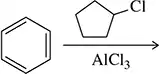
Problem 32d
Predict the product of the following Friedel–Crafts alkylation reactions. Assume only one alkyl group adds in each case.
(d)
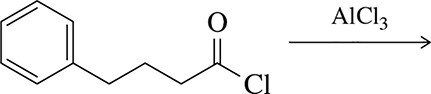
Problem 33b
Predict the product of the following Friedel–Crafts acylation reactions.
(b)
Problem 37
In Section 23.7.4, we learned that Friedel–Crafts alkylation suffers from overalkylation.
(a) Draw the product of a Friedel–Crafts reaction that resulted in three methyl groups adding to the ring.
(b) Why is hard to stop at the addition of one alkyl group?
Problem 39
With a small electron-donating group on the ring, it is possible to get as much as a 2:1 ratio of ortho to para. Why might this be?
Problem 40b
Predict the major product of the following electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions.
(b)
Problem 43b
Predict the products of the following electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions.
(b)
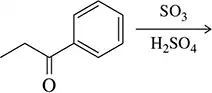
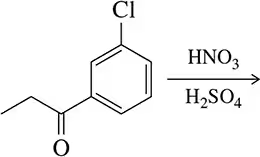
Problem 45c
Predict the major product of the following electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions.
(c)
Problem 46d
Beginning with benzene, synthesize the following substituted benzenes. The ideal number of steps is indicated.
(d)
Problem 53c
Predict the products of the following nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions.
(c)
Problem 55
Assume that Ha is the proton removed in the first step of the benzyne mechanism with p-chlorotoluene. Draw the benzyne intermediate and identify the two products that will result.