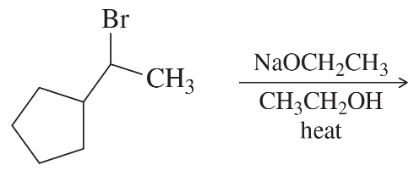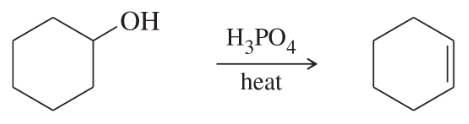Back
BackProblem 30b
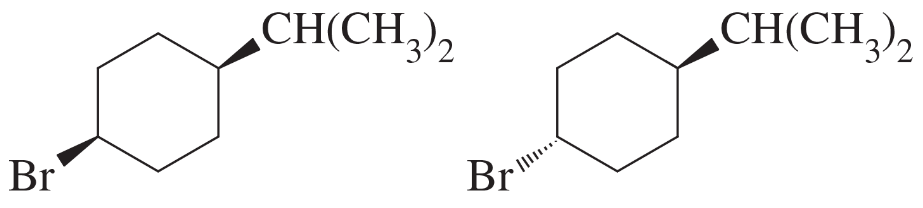
Predict which of the following compounds will undergo elimination with KOH faster, and explain why. Predict the major product that will be formed.
Problem 31a
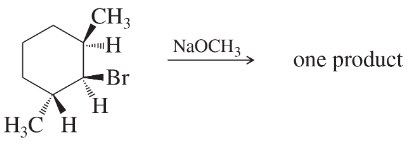
Give the expected product(s) of E2 elimination for each reaction. (Hint: Use models!)
(a)
Problem 31b
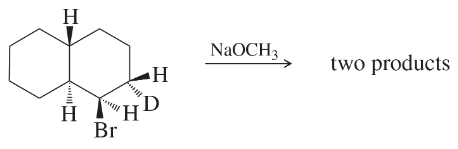
Give the expected product(s) of E2 elimination for each reaction. (Hint: Use models!)
(b)
Problem 32a
Predict the major and minor elimination products of the following proposed reactions (ignoring any possible substitutions for now). In each case, explain whether you expect the mechanism of the elimination to be E1 or E2.
(a)
Problem 32b
Predict the major and minor elimination products of the following proposed reactions (ignoring any possible substitutions for now). In each case, explain whether you expect the mechanism of the elimination to be E1 or E2.
(b)
Problem 33a
Predict the products and mechanisms of the following reactions. When more than one product or mechanism is possible, explain which are most likely.
a. 1−bromohexane + sodium ethoxide in ethanol
Problem 33b
Predict the products and mechanisms of the following reactions. When more than one product or mechanism is possible, explain which are most likely.
b. 2−chlorohexane + NaOCH3 in methanol
Problem 33e,f
Predict the products and mechanisms of the following reactions. When more than one product or mechanism is possible, explain which are most likely.
e. isobutyliodide + KOH in ethanol/water
f. isobutylchloride + AgNO3 in ethanol/water
Problem 33g
Predict the products and mechanisms of the following reactions. When more than one product or mechanism is possible, explain which are most likely.
g. 1−bromo−1−methylcyclopentane + NaOEt in ethanol
Problem 33h
Predict the products and mechanisms of the following reactions. When more than one product or mechanism is possible, explain which are most likely.
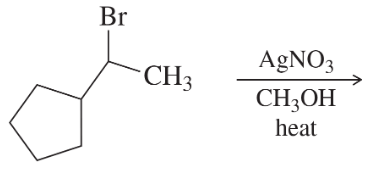
h. 1-bromo-1-methylcyclopentane heated in methanol
Problem 34a
Propose mechanisms for the following reactions.
(a)
Problem 34b
Propose mechanisms for the following reactions.
(b)
Problem 34c
Propose mechanisms for the following reactions.
(c)
Problem 34d
Propose mechanisms for the following reactions.
(d)
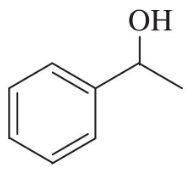
Problem 35a
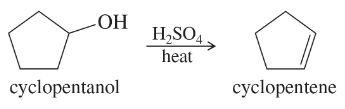
Show the product(s) you expect from dehydration of the following alcohols when they are heated in sulfuric or phosphoric acid. In each case, use a mechanism to show how the products are formed.
(a)
Problem 35b
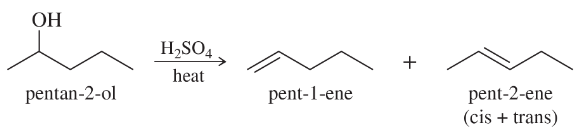
Show the product(s) you expect from dehydration of the following alcohols when they are heated in sulfuric or phosphoric acid. In each case, use a mechanism to show how the products are formed.
(b)
Problem 35c
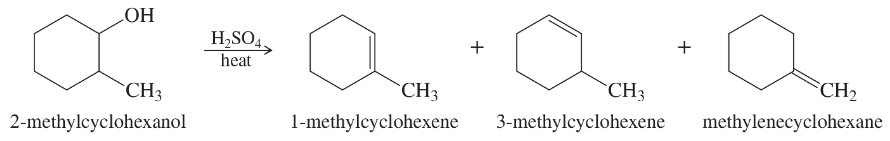
Show the product(s) you expect from dehydration of the following alcohols when they are heated in sulfuric or phosphoric acid. In each case, use a mechanism to show how the products are formed.
(c)
Problem 36a
The dehydrogenation of butane to trans-but-2-ene has ΔH° = +116 kJ/mol (+27.6 kcal/mol) and ΔS° = +117J/kelvin-mol (+28.0 cal/kelvin-mol).
a. Compute the value of ΔG° for dehydrogenation at room temperature (25 °C or 298 °K). Is dehydrogenation favored or disfavored?
HINT: When you are doing synthesis problems, avoid using these high-temperature industrial methods. They require specialized equipment, and they produce variable mixtures of products.
Problem 37a
For practice in recognizing mechanisms, classify each reaction according to the type of mechanism you expect:
1. Free-radical chain reaction
2. Reaction involving strong bases and strong nucleophiles
3. Reaction involving strong acids and strong electrophiles
(a)
Problem 37b
For practice in recognizing mechanisms, classify each reaction according to the type of mechanism you expect:
1. Free-radical chain reaction
2. Reaction involving strong bases and strong nucleophiles
3. Reaction involving strong acids and strong electrophiles
(b)
Problem 37c
For practice in recognizing mechanisms, classify each reaction according to the type of mechanism you expect:
1. Free-radical chain reaction
2. Reaction involving strong bases and strong nucleophiles
3. Reaction involving strong acids and strong electrophiles
(c)
Problem 37d
For practice in recognizing mechanisms, classify each reaction according to the type of mechanism you expect:
1. Free-radical chain reaction
2. Reaction involving strong bases and strong nucleophiles
3. Reaction involving strong acids and strong electrophiles.
(d)
Problem 38a
Propose mechanisms for the following reactions. Additional products may be formed, but your mechanism only needs to explain the products shown.
(a)
(Hint: Hydride shift)
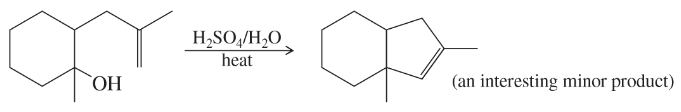
Problem 38c
Propose mechanisms for the following reactions. Additional products may be formed, but your mechanism only needs to explain the products shown.
(c)
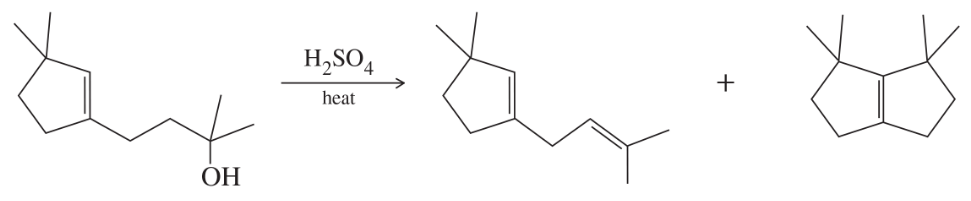
Problem 39a
Propose mechanisms for the following reactions.
(a)
HINT: Alcohol dehydrations usually go through E1 elimination of the protonated alcohol, with a carbocation intermediate. Rearrangements are common.
Problem 39b
Propose mechanisms for the following reactions.
(b)
HINT: Alcohol dehydrations usually go through E1 elimination of the protonated alcohol, with a carbocation intermediate. Rearrangements are common.
Problem 39d
Propose mechanisms for the following reactions.
d.
HINT: Alcohol dehydrations usually go through E1 elimination of the protonated alcohol, with a carbocation intermediate. Rearrangements are common.
Problem 40a,b,c
Draw a structure for each compound (includes old and new names).
a. 3-methylpent-1-ene
b. cis-3-methyl-3-hexene
c. 3,4-dibromobut-1-ene
Problem 40d,e,f
Draw a structure for each compound (includes old and new names).
d. 1,3-cyclohexadiene
e. cycloocta-1,4-diene
f. (Z)-3-methyl-2-octene
Problem 40g,h
Draw a structure for each compound (includes old and new names).
g. vinylcyclopropane
h. (Z)-2-bromo-2-pentene