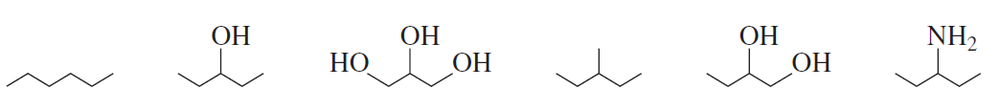Back
Back Bruice 8th Edition
Bruice 8th Edition Ch.3 - An Introduction to Organic Compounds:Nomenclature, Physical Properties, and Structure
Ch.3 - An Introduction to Organic Compounds:Nomenclature, Physical Properties, and StructureProblem 29c
Draw condensed and skeletal structures for each of the following amines:
c. 5-methyl-1-hexanamine
Problem 29e
Draw condensed and skeletal structures for each of the following amines:
e. N,N-dimethyl-3-pentanamine
Problem 29f
Draw condensed and skeletal structures for each of the following amines:
f. cyclohexylethylmethylamine
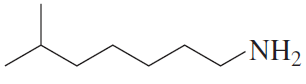
Problem 30a
For each of the following, give the systematic name and the common name (if it has one) and then indicate whether it is a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine:
a.
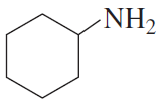
Problem 30b
For each of the following, give the systematic name and the common name (if it has one) and then indicate whether it is a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine:
b.
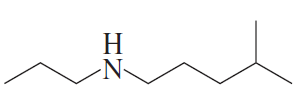
Problem 30c
For each of the following, give the systematic name and the common name (if it has one) and then indicate whether it is a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine:
c.
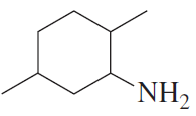
Problem 30d
For each of the following, give the systematic name and the common name (if it has one) and then indicate whether it is a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine:
d.
Problem 31a
Predict the approximate size of the following bond angles.
(a) the C—O—C bond angle in an ether
Problem 31b
Predict the approximate size of the following bond angles.
(b) the C—N—C bond angle in a secondary amine
Problem 31d
Predict the approximate size of the following bond angles.
(d) the C—N—C bond angle in a quaternary ammonium salt
Problem 32
What is the smallest straight-chain alkane that is a liquid at room temperature (which is about 25 °C)?
Problem 33a(1,2,3)
Which of the following compounds forms hydrogen bonds between its molecules?
1. CH3CH2OCH2CH2OH
2. CH3CH2N(CH3)2
3. CH3CH2CH2CH2Br
Problem 33b(1,2,3)
Which of the preceding compounds forms hydrogen bonds with a solvent such as ethanol?
1. CH3CH2OCH2CH2OH
2. CH3CH2N(CH3)2
3. CH3CH2CH2CH2Br
Problem 33b(4,5,6)
Which of the preceding compounds forms hydrogen bonds with a solvent such as ethanol?
4. CH3CH2CH2NHCH3
5. CH3CH2CH2COOH
6. CH3CH2CH2CH2F
Problem 34a,b
Explain why
a. H2O (100 °C) has a higher boiling point than CH3OH 165 °C2.
b. H2O (100 °C) has a higher boiling point than NH3 (-33 °C).
Problem 34c,d
Explain why
c. H2O (100 °C) has a higher boiling point than HF 120 °C2.
d. HF 120 °C2 has a higher boiling point than NH3 (-33 °C).
Problem 35
Rank the following compounds from highest boiling to lowest boiling:
Problem 37
In which solvent would cyclohexane have the lowest solubility: 1-pentanol, diethyl ether, ethanol, or hexane?
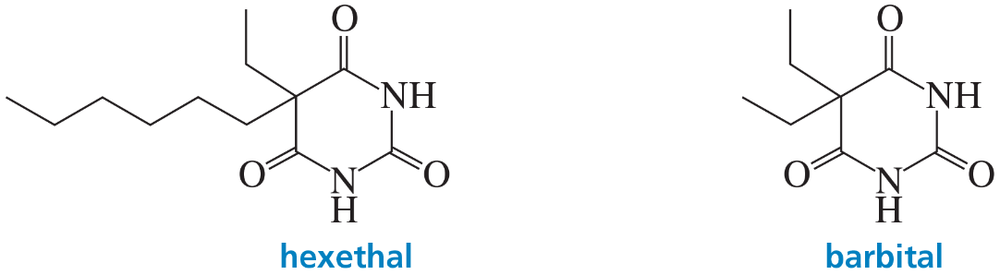
Problem 39
The effectiveness of a barbiturate as a sedative is related to its ability to penetrate the nonpolar membrane of a cell. Which of the following barbiturates would you expect to be the more effective sedative?
Problem 40a
Draw all the staggered and eclipsed conformers that result from rotation about the C-2-C-3 bond of pentane.
Problem 40b
Draw a potential-energy diagram for rotation about the C-2---C-3 bond of pentane through 360°, starting with the least stable conformer.
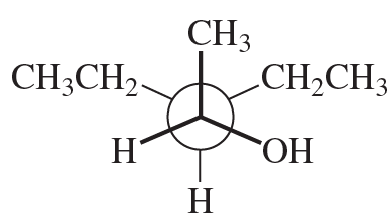
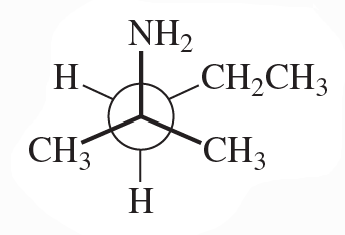
Problem 41
Convert the following Newman projections to skeletal structures and name them.
a.
b.
Problem 42a
Using Newman projections, draw the most stable conformer for each of the following:
a. 3-methylpentane, viewed along the C-2---C-3 bond
Problem 42b
Using Newman projections, draw the most stable conformer for each of the following:
b. 3-methylhexane, viewed along the C-3----C-4 bond
Problem 42c
Using Newman projections, draw the most stable conformer for each of the following:
c. 3,3-dimethylhexane, viewed along the C-3---C-4 bond
Problem 43
The bond angles in a regular polygon with n sides are equal to 180° - 360°/n
a. What are the bond angles in a regular octagon?
b. What are the bond angles in a regular nonagon?
Problem 44
Verify the strain energy shown in Table 3.8 for cycloheptane
Problem 45
Draw 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexachlorocyclohexane with
a. all the chloro groups in axial positions.
b. all the chloro groups in equatorial positions.
Problem 46
Using the data in Table 3.9, calculate the percentage of molecules of cyclohexanol that have the OH group in an equatorial position at 25 °C.
Problem 47
The chair conformer of fluorocyclohexane is 0.25 kcal/mol more stable when the fluoro substituent is in an equatorial position than when it is in an axial position. How much more stable is the anti conformer than a gauche conformer of 1-fluoropropane, considering rotation about the C1−C2 bond?