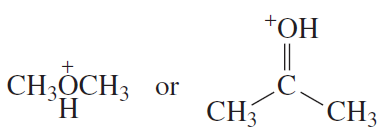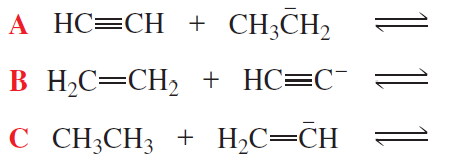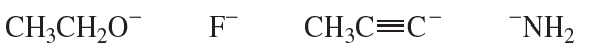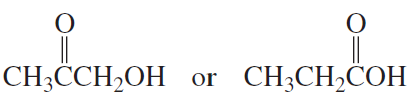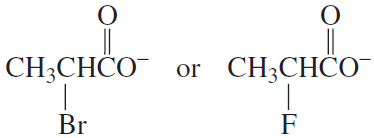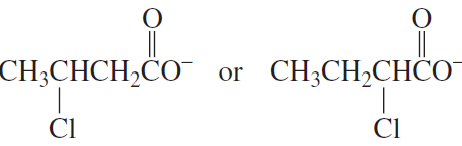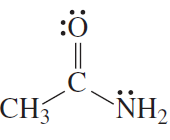Back
BackProblem 1
Which of the following are not acids?
CH3COOH, CO2 , HNO2 , HCOOH, CCl4
Problem 2a,b
Consider the following reaction: HBr + -C≡N ⇌ Br− + HC≡N
a. What is the acid on the left side of the equation?
b. What is the base on the left side of the equation?
Problem 2c,d
Consider the following reaction:
HBr + -C≡N ⇌ Br− + HC≡N
c. What is the conjugate base of the acid on the left?
d. What is the conjugate acid of the base on the left?
Problem 2g,h
Consider the following reaction:
HBr + -C≡N ⇌ Br− + HC≡N
g. What is the conjugate base of the acid on the right?
h. What is the conjugate acid of the base on the right?
Problem 4a
What is the conjugate acid of each of the following?
1. NH3
2. Cl−
3. HO−
4. H2O
Problem 4b
What is the conjugate base of each of the following?
1. NH3
2. HBr
3. HNO3
4. H2O
Problem 5ab
a. Which is a stronger acid: one with a pKa of 5.2 or one with a pKa of 5.8?
b. Which is a stronger acid: one with an acid dissociation constant of 3.4 × 10−3 or one with an acid dissociation constant of 2.1 × 10−4?
Problem 6a
An acid has a Ka of 4.53 × 10−6 in water. What is its Keq for reaction with water in a dilute solution? ([H2O] = 55.5 M)
Problem 7a
Butyric acid, the compound responsible for the unpleasant odor and taste of sour milk, has a pKa value of 4.82. What is its Ka value? Is it a stronger acid or a weaker acid than vitamin C?
Problem 8a
Antacids are compounds that neutralize stomach acid. Write the equations that show how Milk of Magnesia, Alka-Seltzer, and Tums remove excess acid.
a. Milk of Magnesia: Mg(OH)2
b. Alka-Seltzer: KHCO3 and NaHCO3
c. Tums: CaCO3
Problem 10a,b,c
Draw the conjugate acid of each of the following:
a. CH3CH2OH
b. CH3CH2O−
c.
Problem 12c,d
Estimate the pKa values of the following compounds:
c. CH3CH2COOH
d. CH3CH2CH2N+H3
Problem 13
a. Which is a stronger base: CH3COO− or HCOO−? (The pKa of CH3COOH is 4.8; the pKa of HCOOH is 3.8.)
b. Which is a stronger base: HO− or -NH2? (The pKa of H2O is 15.7; the pKa of NH3 is 36.)
c. Which is a stronger base: H2O or CH3OH? (The pKa of H3O+ is −1.7; the pKa of CH3O+H2 is −2.5.)
Problem 15
Does methanol behave as an acid or a base when it reacts with methylamine?
Problem 16a(1,2)
For each of the acid–base reactions in [Section 2.3], compare the pKa values of the acids on either side of the equilibrium arrows to prove that the equilibrium lies in the direction indicated.
1. <IMAGE>
2. <IMAGE>
Problem 16a(3,4)
For each of the acid–base reactions in [Section 2.3], compare the pKa values of the acids on either side of the equilibrium arrows to prove that the equilibrium lies in the direction indicated.
3. <IMAGE>
4. <IMAGE>
Problem 17a
Ethyne (HC≡CH) has a pKa value of 25, water has a pKa value of 15.7, and ammonia (NH3) has a pKa value of 36. Draw the equation, showing equilibrium arrows that indicate whether reactants or products are favored, for the acid–base reaction of ethyne with
a. HO-.
Problem 17b,c
Ethyne (HC≡CH) has a pKa value of 25, water has a pKa value of 15.7, and ammonia (NH3) has a pKa value of 36. Draw the equation, showing equilibrium arrows that indicate whether reactants or products are favored, for the acid–base reaction of ethyne with
b. −NH2.
c. Which would be a better base to use if you wanted to remove a proton from ethyne, HO− or -NH2?
Problem 18a
Which of the following bases can remove a proton from acetic acid in a reaction that favors products?
HO− CH3NH2 HC≡C− CH3OH H2O Cl−
Problem 19c,d
Calculate the equilibrium constant for the acid–base reaction between the reactants in each of the following pairs:
c. CH3NH2 + H2O
d. CH3N+H3 + H2O
Problem 20a
Rank the ions (−CH3, −NH2, HO−, and F−) from most basic to least basic.
Problem 21
Rank the carbanions shown in the margin from most basic to least basic.
<IMAGE>
Problem 22
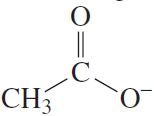
Which is a stronger acid?
Problem 24
Which reaction in Problem 23 has the smallest equilibrium constant?
Problem 24b
Rank the following from strongest base to weakest base:
b.
Problem 27c,d
Which is a stronger acid?
c. <IMAGE>
d. CH3CH2CH2OH or CH3CH2CH2SH
Problem 30c,d
Which is a stronger acid?
c. CH3OCH2CH2CH2OH or CH3CH2OCH2CH2OH
d.
Problem 32a,b
Which is a stronger base?
a.
b.
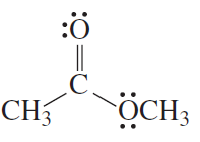
Problem 33
If HCl is a weaker acid than HBr, why is ClCH2COOH a stronger acid than BrCH2COOH?
Problem 34a,b
For each of the following compounds, indicate the atom that is protonated when an acid is added to a solution of the compound.
a.
b.