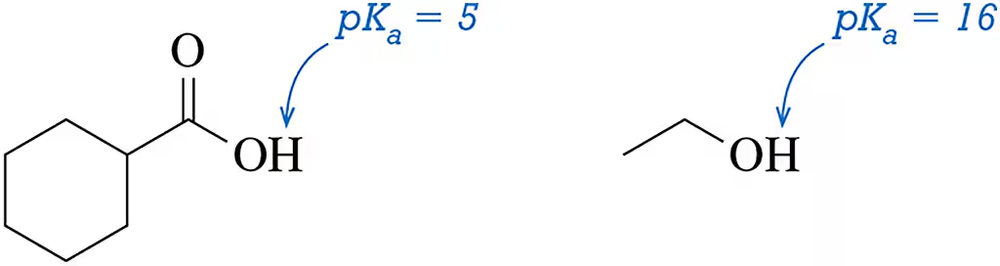Back
BackProblem 1
A carboxylic acid ( pKa = 5) is 1011 times more acidic than an alcohol (pKa = 16). Why?
Problem 2
What reagent would you use to brominate the allylic carbon of cyclohexene?
Problem 3
Provide an arrow-pushing mechanism for the following alkane bromination. [Don't forget to use fishhook arrows to represent the movement of single electrons.]
Problem 4
Calculate the oxidation number of the indicated atoms in the following reaction.
Problem 5
Which haloalkane would you expect to undergo the fastest SN1 reaction? Why?
Problem 6
What is the product of the following reaction?
Problem 7
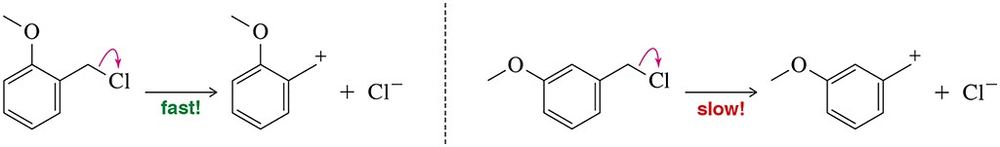
Look closely at the resonance structures of the benzylic anions, radicals, and cations in Figures 24.2–24.4. On which benzene carbons did the charge/radical exist in the resonance structures—that is, were they ortho, meta, or para?
Problem 8
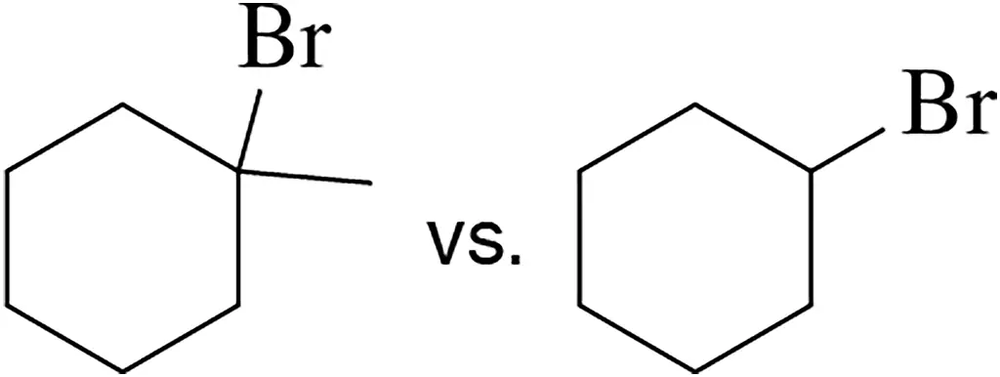
Rationalize the rate difference in carbocation formation for the following molecules.
Problem 9
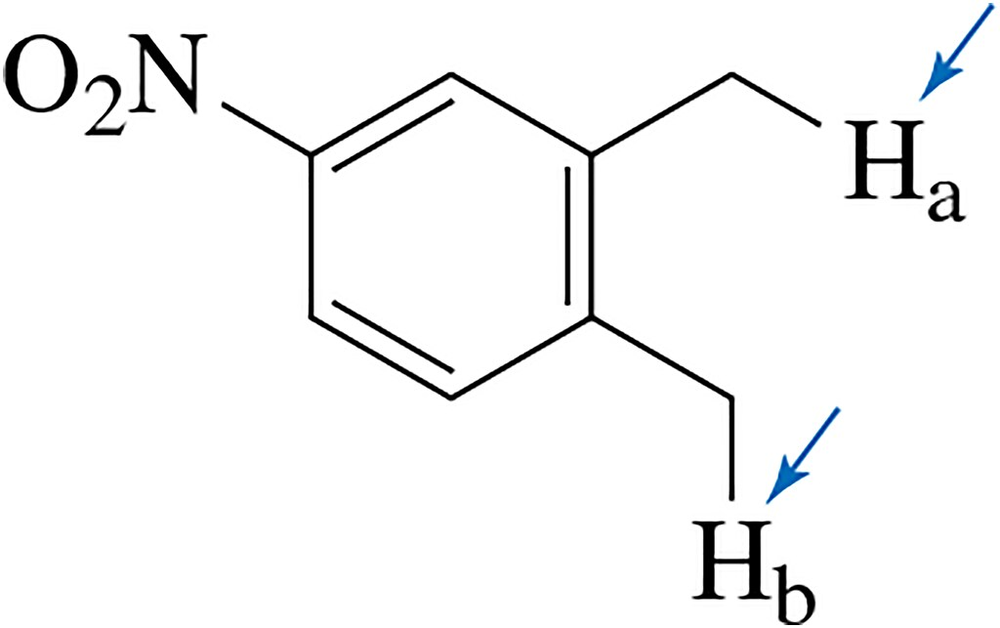
Which proton, Ha or Hb, would you expect to have the lower pKa value?
Problem 11a
Though the nitro group is electron-withdrawing by resonance, when in the meta position, it doesn’t communicate by resonance with the phenoxide anion. And yet, the pKₐ value of m-nitrophenol is lowered from 10 (the pKₐ value of unsubstituted phenol) to 8.4. Explain this observation.
Problem 15
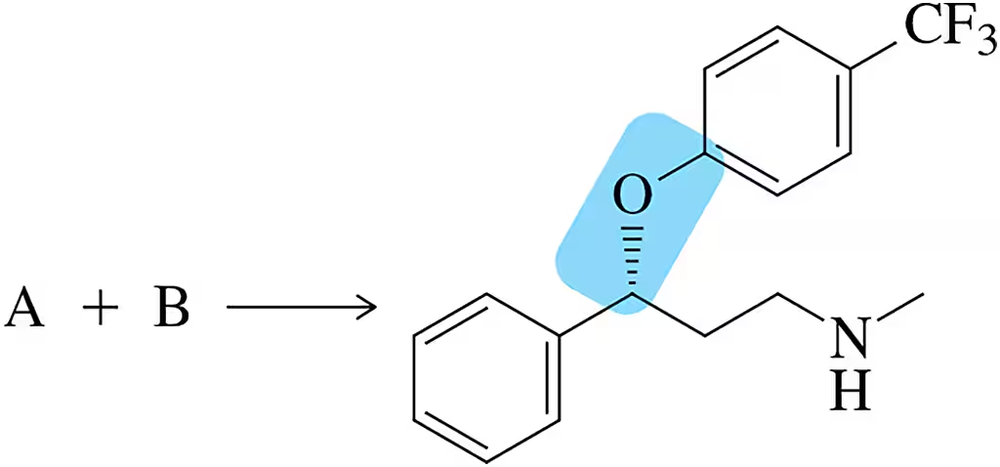
Fluoxetine hydrochloride (Prozac®) is a widely used antidepressant. How might you stereoselectively install the indicated ether functional group (ROR) in (R)-fluoxetine?
Problem 16a
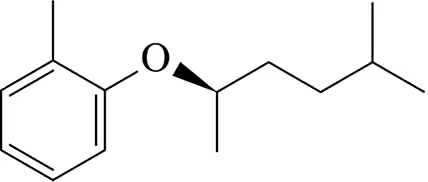
Suggest a phenoxide and an alkyl halide to make the following aryl alkyl ethers.
(a)
Problem 16b
Suggest a phenoxide and an alkyl halide to make the following aryl alkyl ethers.
(b)
Problem 17
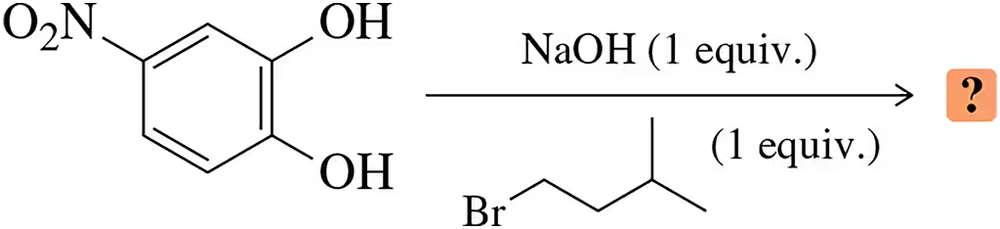
Predict the product when the dihydroxybenzene shown is treated with a single equivalent of both base and haloalkane.
Problem 18a
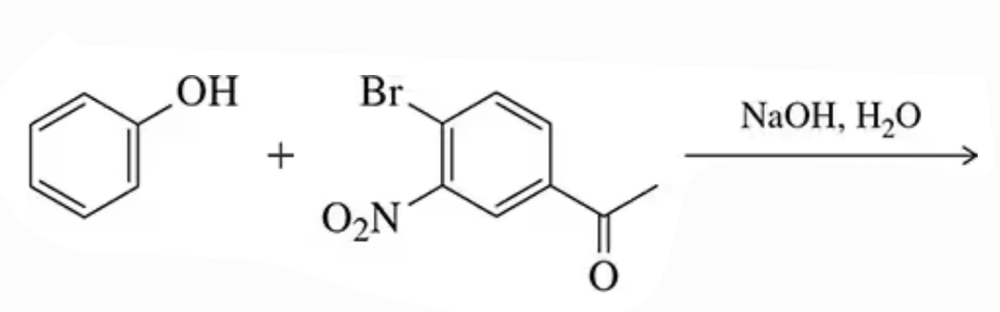
Predict the product of the following substitution/addition reactions involving phenoxides.
(a)
Problem 18d
Predict the product of the following substitution/addition reactions involving phenoxides. [Because this problem represents a review of current and previous material, section numbers have been provided for your reference.]
(d)
Problem 21
In light of Figure 24.22, provide a mechanism by which para-dihydroxybenzene is oxidized to para-quinone.
Problem 22
(a) Based on Figure 24.23, explain why meta-dihydroxybenzene is not oxidized to meta-quinone.
(b) If a meta-quinone is not produced, what would you expect the product of the oxidation of meta-dihydroxybenzene to be?
Problem 23
Assessment 24.22 asked why meta-dihydroxybenzene could not be oxidized to meta-quinone. The attempted oxidation instead gives rise to three different quinone products. Suggest a mechanism for the formation of each.
Problem 24a
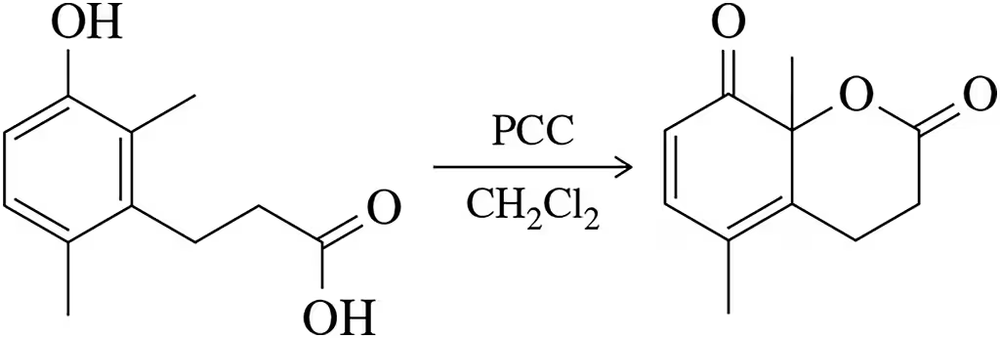
Oxidation of a phenol derivative produces the lactone shown. Provide an arrow-pushing mechanism that rationalizes this outcome.
Problem 24.47a
FROM THE LITERATURE The following steps were used in the synthesis of the antimalarial thiaplakortone A. Identify the missing reagents, (a) and (b),
<IMAGE>
Problem 25c
Suggest reagents and reaction conditions that would result in synthesis of the following bromoalkanes.
(c)
Problem 26a
Predict the product(s) of each of the following multistep reactions.
(a)
Problem 26b
Predict the product(s) of each of the following multistep reactions.
(b)
Problem 29
Using Equation 5.8, calculate the difference in transition state energies that lead to the rate differences shown in Figure 24.35.
Problem 30
Predict the product for the following substitution reactions. Indicate whether each reaction likely proceeds by an SN1 or SN2 mechanism.
(a)
Problem 30b
Predict the product for the following substitution reactions. Indicate whether each reaction likely proceeds by an SN1 or SN2 mechanism.
(b)
Problem 30c
Predict the product for the following substitution reactions. Indicate whether each reaction likely proceeds by an SN1 or SN2 mechanism.
(c)
Problem 31
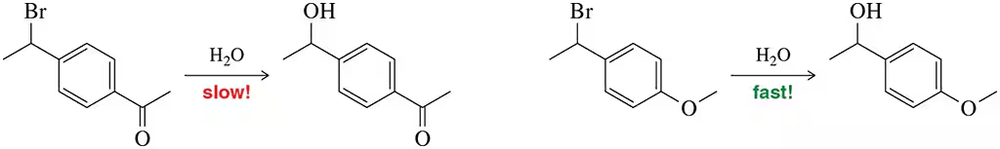
Substitution at the benzylic position of the molecules shown was observed to occur at different rates. Explain this observation.
Problem 32a
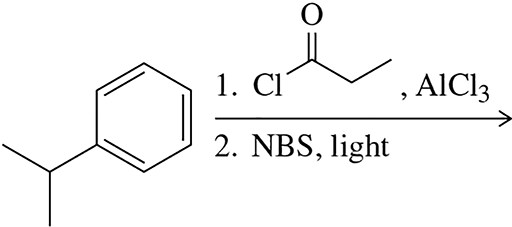
Predict the product of the following series of reactions.
(a)