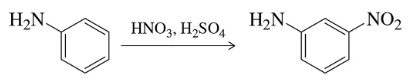Back
BackProblem 1
Draw the Lewis structure of azidomethane (CH3N3) [Show two important resonance structures.]
Problem 2
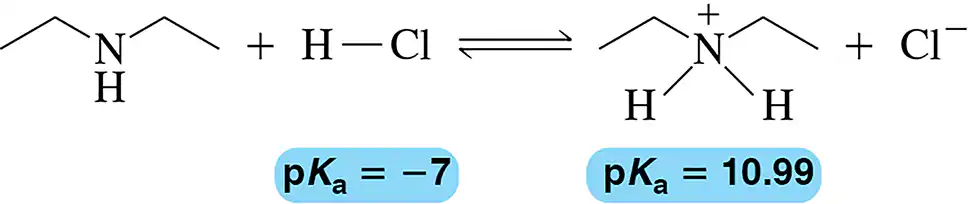
Predict the Keq for the following acid–base reaction.
Problem 3
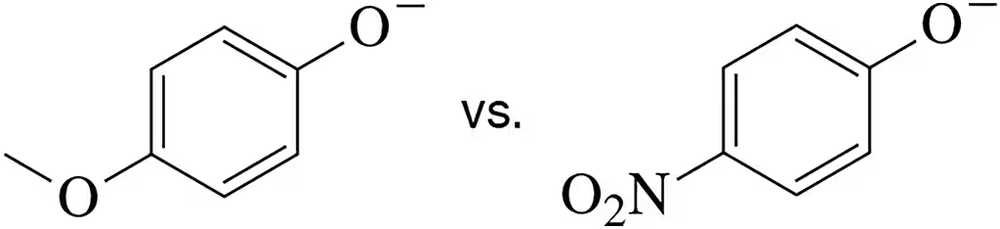
Which of the following phenoxides should be a stronger nucleophile?
Problem 5
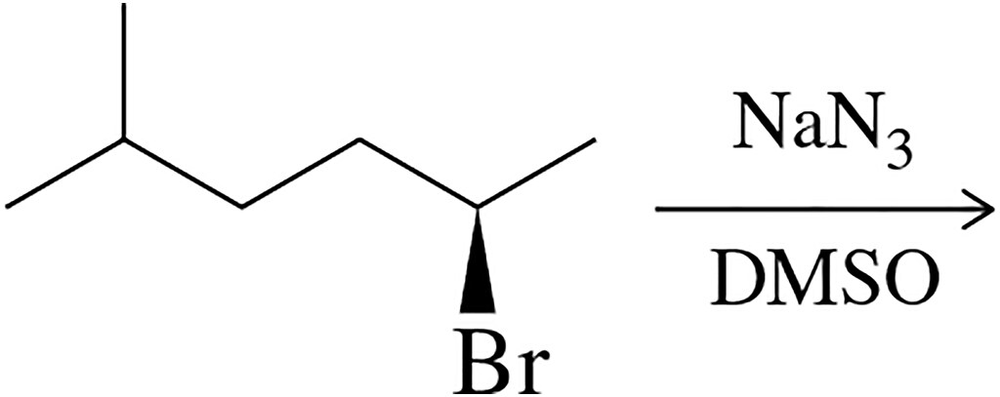
Would you expect the following substitution reaction to proceed with inversion or racemization? Why?
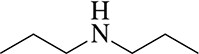
Problem 7a
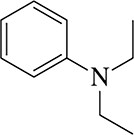
Give an acceptable name for each amine.
(a)
Problem 7b
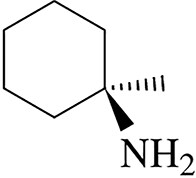
Give an acceptable name for each amine.
(b)
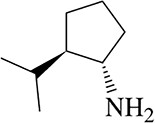
Problem 7c
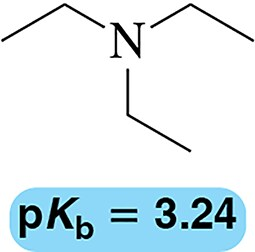
Give an acceptable name for each amine.
(c)
Problem 8c
Given the following names, draw the structure of the molecule.
c. (S)-2-methyloctan-4-amine
Problem 9
Label the amines shown as a 1° amine, 2° amine, 3° amine, or 4° ammonium ion.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Problem 10
Draw a constitutional isomer for C4H11N containing a 1° amine at a
(a) 1° carbon,
(b) 2° carbon, and
(c) 3° carbon.
Problem 15
We usually calculate Keq for acid–base reactions using pKa values.
(a) Derive an equation to calculate Keq using pKb values, then
(b) use it to calculate the equilibrium constant for the following reaction.
Problem 20
Which would you expect to be a stronger nucleophile, ethyl amine or diethyl amine? Why?
Problem 25c
Predict the product of the following reactions.
(c)
Problem 28b
Given the starting reactant, suggest a method for synthesizing the amine on the right.
(b)
Problem 29
The nitro group directs electrophilic aromatic substitution to the meta position. After reduction by hydrogenation, to which carbon(s) does it direct?
Problem 31b
Following a LiAlH₄ reduction, an IR spectrum suggested that the product was a mixture of the starting amide and the desired amine.
(b) Once separated, how could you distinguish between the amide and the amine using IR spectroscopy?
Problem 46b
Given the pKb, calculate the pKa of the conjugate acid.
(b)
Problem 46c
Given the pKb, calculate the pKa of the conjugate acid.
(c)
Problem 47b
Calculate the equilibrium constant for each of the acid–base reactions shown.
b.
Problem 52
Despite the amino group being an ortho/para director, nitration of aniline gives the meta isomer predominantly. Explain this result.
Problem 55b
Predict the product(s) of the reactions shown.
(b)
Problem 55i
Predict the product(s) of the reactions shown.
(i)
Problem 55j
Predict the product(s) of the reactions shown.
(j)
Problem 56b
Suggest reagents to carry out the following transformations. Some may require more than one step.
(b)
Problem 57
The Gabriel synthesis is most frequently done with 1° alkyl halides. Why is it less successful with more substituted halides?
Problem 67
The final step in the synthesis of diazoxide, a drug used to treat low blood pressure, is shown here. Suggest a mechanism for this step.
Problem 68
The synthesis of ⍺-hydroxy acids can be done starting with amino acids. Suggest a mechanism of the two-step transformation shown. [The alcohol oxygen is the same in the reactant and product.