Back
BackProblem 74
Find the slope of the line passing through each pair of points or state that the slope is undefined. Assume that all variables represent positive real numbers. Then indicate whether the line through the points rises, falls, is horizontal, or is vertical. (-a, 0) and (0, -b)
Problem 78
Give the slope and y-intercept of each line whose equation is given. Assume that B ≠ 0. Ax = By - C
Problem 79
Find the value of y if the line through the two given points is to have the indicated slope. (3, y) and (1, 4), m = −3
Problem 82
Graph each linear function. 6x-5f(x) - 20 = 0
Problem 84
If one point on a line is (2, −6) and the line's slope is -3/2, find the y-intercept.
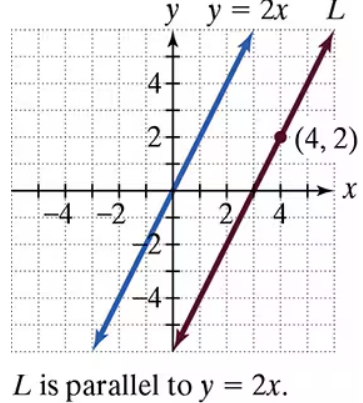
Problem 1
Write an equation for line L in point-slope form and slope-intercept form.
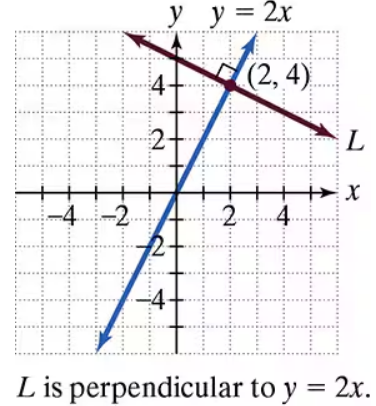
Problem 3
Write an equation for line L in point-slope form and slope-intercept form.
Problem 5
Use the given conditions to write an equation for each line in point-slope form and slope-intercept form. Passing through (−8, −10) and parallel to the line whose equation is y = −4x + 3
Problem 7
Use the given conditions to write an equation for each line in point-slope form and slope-intercept form. Passing through (2, −3) and perpendicular to the line whose equation is y = (1/5)x + 6
Problem 9
Use the given conditions to write an equation for each line in point-slope form and general form. Passing through (−2, 2) and parallel to the line whose equation is 2x-3y-7=0
Problem 11
Use the given conditions to write an equation for each line in point-slope form and general form. Passing through (4, −7) and perpendicular to the line whose equation is x − 2y – 3 = 0
Problem 13
Find the average rate of change of the function from x1 to x2. f(x) = 3x from x1 = 0 to x2 = 5
Problem 15
Find the average rate of change of the function from x1 to x2. f(x) = x² + 2x from x1 = 3 to x2 = 5
Problem 17
Find the average rate of change of the function from x1 to x2. f(x) = √x from x1 = 4 to x2 = 9
Problem 19
Write an equation in slope-intercept form of a linear function f whose graph satisfies the given conditions. The graph of ƒ passes through (−1, 5) and is perpendicular to the line whose equation is x = 6.
Problem 20
Write an equation in slope-intercept form of a linear function f whose graph satisfies the given conditions. The graph of ƒ passes through (−2, 6) and is perpendicular to the line whose equation is x = -4.
Problem 21
Write an equation in slope-intercept form of a linear function f whose graph satisfies the given conditions. The graph of ƒ passes through (−6, 4) and is perpendicular to the line that has an x intercept of 2 and a y-intercept of -4.
Problem 45
After a 30% price reduction, you purchase a 50″ 4K UHD TV for $245. What was the television's price before the reduction?
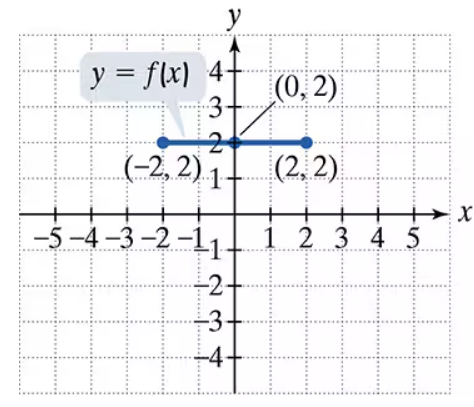
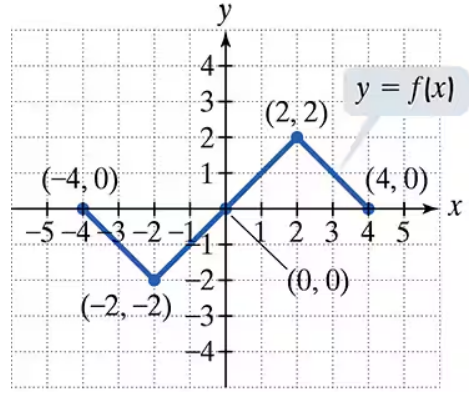
Problem 1
Use the graph of y = f(x) to graph each function g.
g(x) = f(x)+1
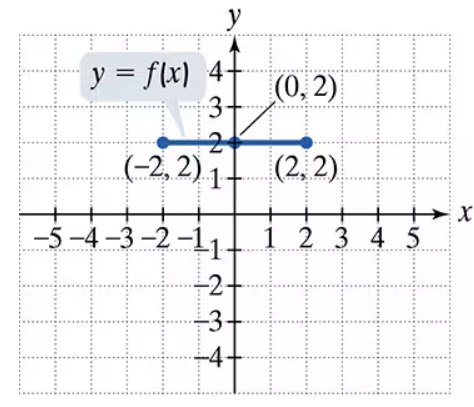
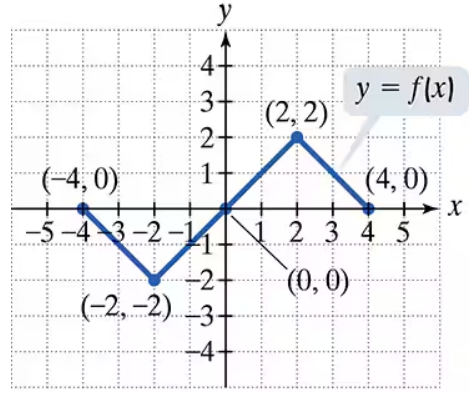
Problem 3
Use the graph of y = f(x) to graph each function g.
g(x) = f(x+1)
Problem 5
Use the graph of y = f(x) to graph each function g.
g(x) = f(x-1) - 2
Problem 19
use the graph of y = f(x) to graph each function g.
g(x) = f(x-1)
Problem 21
Use the graph of y = f(x) to graph each function g.
g(x) = f(x-1)+2
Problem 33
Use the graph of y = f(x) to graph each function g. g(x) = f(x)+2
Problem 47
Use the graph of y = f(x) to graph each function g. g(x) = -f(x-1) + 1
Problem 55
Begin by graphing the standard quadratic function, f(x) = x². Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. g(x) = (x − 2)²
Problem 57
Begin by graphing the standard quadratic function, f(x) = x². Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. h(x) = -(x − 2)²
Problem 66
Begin by graphing the standard quadratic function, f(x) = x². Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. h(x) = -2(x+2)²+1