Back
Back Mullins 1st Edition
Mullins 1st Edition Ch. 11 - Properties and Synthesis of Alkyl Halides: Radical Reactions
Ch. 11 - Properties and Synthesis of Alkyl Halides: Radical ReactionsProblem 2
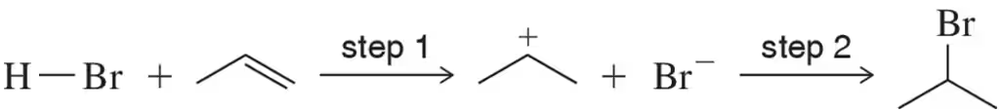
Show the transition state of each step of the following alkene addition reaction. Be sure to indicate whether the transition state in each is reactant-like or product-like.
Problem 3
Using the bond-dissociation energies in Table 5.6 (see Section 5.3.1), estimate the equilibrium constant of the following reaction at 298 K.
Problem 5
Draw all resonance structures of the following carbanion and carbocation.
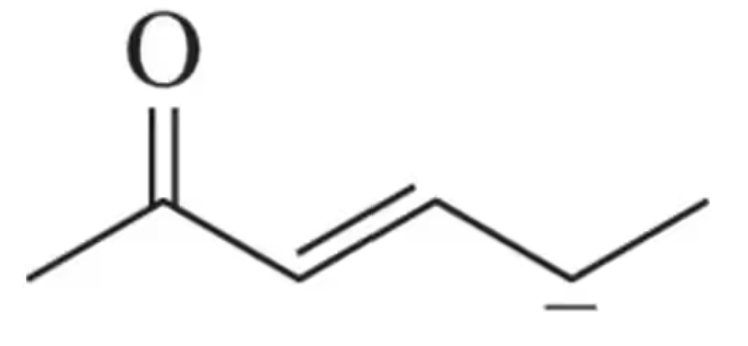
(a)
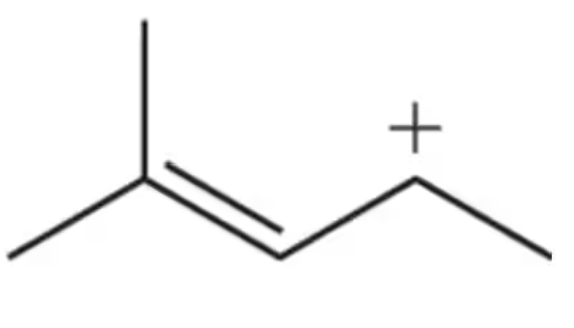
(b)
Problem 6b
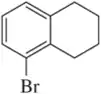
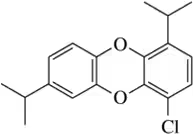
Identify the following halogen-containing compounds as a haloalkane, haloalkene, or haloarene.
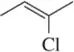
(b)
Problem 6c
Identify the following halogen-containing compounds as a haloalkane, haloalkene, or haloarene.
(c)
Problem 6d
Identify the following halogen-containing compounds as a haloalkane, haloalkene, or haloarene.
(d)
Problem 6e
Identify the following halogen-containing compounds as a haloalkane, haloalkene, or haloarene.
(e)
Problem 6f
Identify the following halogen-containing compounds as a haloalkane, haloalkene, or haloarene.
(f)
Problem 7.20a,c
Suppose you intend to synthesize the secondary alkyl halide from each reaction shown.
(a) What is the atom economy of each reaction?
(c) Which reaction would you consider greener? Why?
Problem 8a
From the IUPAC name, draw the corresponding structure.
(a) (R)-6-iodo-3-isopropylnon-1-ene
Problem 8b
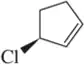
From the IUPAC name, draw the corresponding structure.
(b) (1R,2S)-1-chloro-2-methylcyclobutane
Problem 9a
Classify the following molecules as hydrophilic, hydrophobic, lipophilic, or lipophobic. Each molecule should have two classifications.
(a)
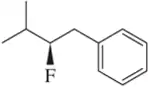
Problem 9b
Classify the following molecules as hydrophilic, hydrophobic, lipophilic, or lipophobic. Each molecule should have two classifications.
(b)
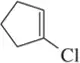
Problem 9d
Classify the following molecules as hydrophilic, hydrophobic, lipophilic, or lipophobic. Each molecule should have two classifications.
(d)
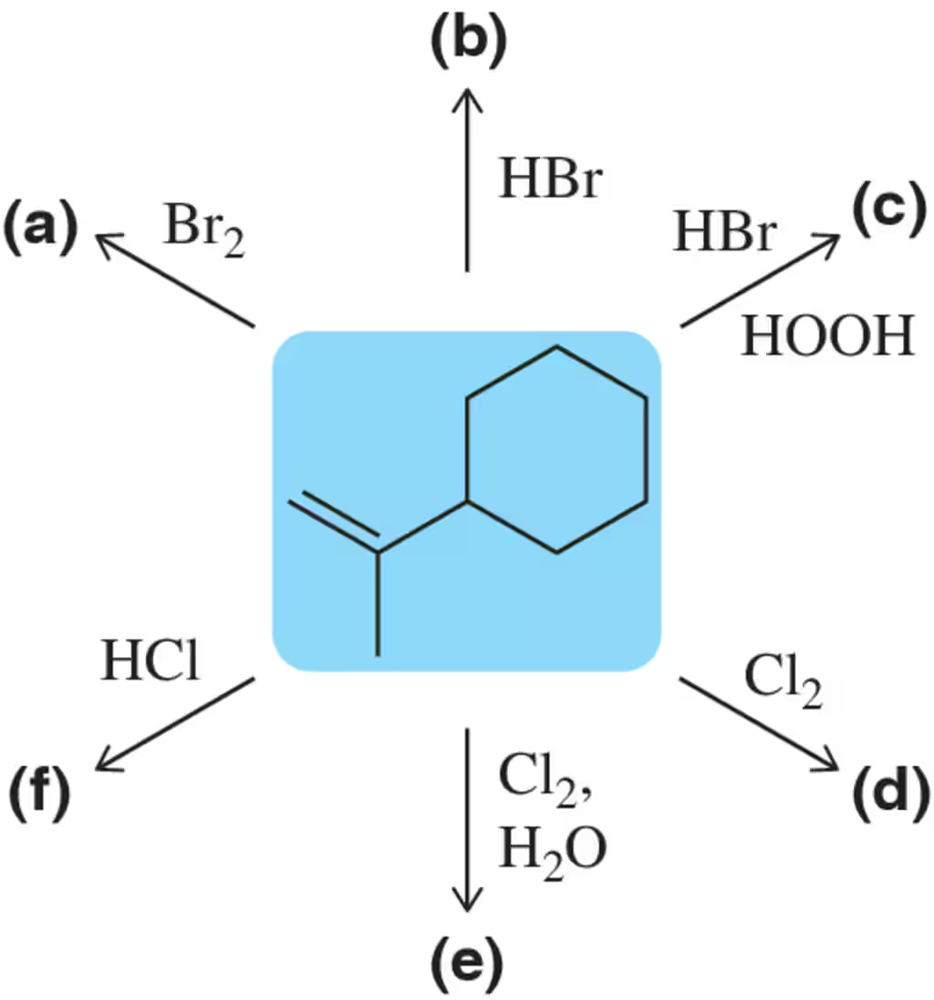
Problem 10a
Predict the product of the following haloalkane syntheses.
(a)
Problem 10c
Predict the product of the following haloalkane syntheses.
(c) HBr↗HOOH
Problem 10e
Predict the product of the following haloalkane syntheses.
(e)
Problem 11
Specify the conditions that would allow the synthesis of the 1° and 3° bromoalkanes from the same starting alkene.
Problem 11.17
The most stable intermediate forms first. Explain this statement by showing a reaction coordinate diagram for the formation of a 3° carbocation over a 2° carbocation in the following alkene addition reaction.
Problem 12
Halohydrin formation is a stereospecific reaction. Identify the products of halohydrin formation of the following diastereomeric alkenes to demonstrate this stereospecificity.
Problem 14
Provide a mechanism for the chlorination of cyclohexane. Be sure to include initiation, propagation, and three possible termination steps.
Problem 15
A radical reaction, as it progressed through its propagation steps, involved the following radical species. Suggest which products might form in all possible termination steps (six products are possible).
Problem 16a
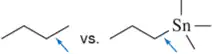
Based on the stability of the radicals produced, predict which bond in each pair would have the higher bond-dissociation energy.
(a)
Problem 16b
Based on the stability of the radicals produced, predict which bond in each pair would have the higher bond-dissociation energy.
(b)
Problem 16c
Based on the stability of the radicals produced, predict which bond in each pair would have the higher bond-dissociation energy.
(c)
Problem 16d
Based on the stability of the radicals produced, predict which bond in each pair would have the higher bond-dissociation energy.
(d)
Problem 18a
Using the bond-dissociation energies in Table 5.6,
(a) predict whether or not a fluorine radical would be selective for forming a single radical from propane.
Problem 18b
Using the bond-dissociation energies in Table 5.6,
(b) Will the transition state be reactant-like or product-like? Explain your answer.
Problem 19a
Using the bond-dissociation energies in Table 5.6,
(a) predict whether or not an iodine radical would be selective for forming a single radical propane.
Problem 20a
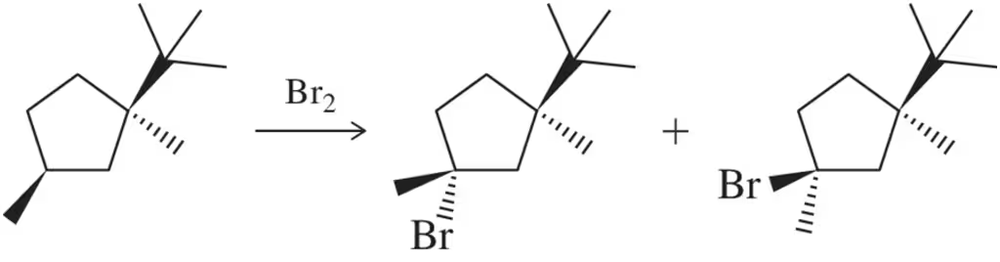
When (1R,3S)-1-tert-butyl-1,3-dimethylcyclopentane is halogenated, one stereoisomer is produced in excess.
(a) Predict the identity of the major stereoisomer