Back
Back Mullins 1st Edition
Mullins 1st Edition Ch. 11 - Properties and Synthesis of Alkyl Halides: Radical Reactions
Ch. 11 - Properties and Synthesis of Alkyl Halides: Radical ReactionsProblem 20b
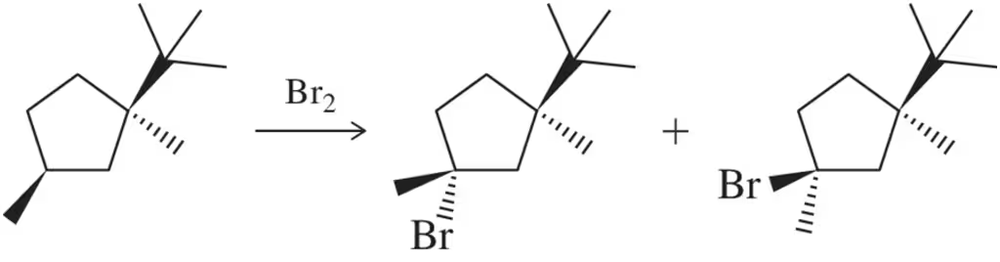
When (1R,3S)-1-tert-butyl-1,3-dimethylcyclopentane is halogenated, one stereoisomer is produced in excess.
(b) explain why this reaction did not produce an equal mixture of stereoisomers.
Problem 21
Suppose a 2-halobutane was needed for a synthetic sequence. Starting your synthesis with butane, would it be best to put a chlorine or bromine at that position? Explain.
Problem 22b
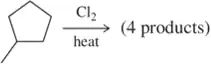
Predict the major products of the following alkane halogenation reactions. [The number of products shown ignores the formation of racemic mixtures.]
(b)
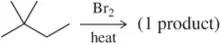
Problem 22c
Predict the major products of the following alkane halogenation reactions. [The number of products shown ignores the formation of racemic mixtures.]
(c)
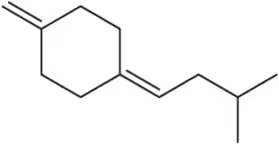
Problem 22d
Predict the major products of the following alkane halogenation reactions. [The number of products shown ignores the formation of racemic mixtures.]
(d)
Problem 23
Can you make a 1° bromoalkane like (3-bromopropyl)cyclopentane using alkane halogenation? Why or why not?
Problem 24a
Why is a 2° carbon radical more stable than a 1° carbon radical?
Problem 25a
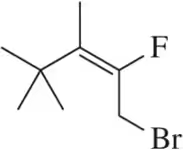
Predict the major products of the following alkene halogenation reactions. [D is the symbol for deuterium, an isotope of hydrogen.]
(a)
Problem 25b
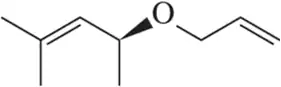
Predict the major products of the following alkene halogenation reactions. [D is the symbol for deuterium, an isotope of hydrogen.]
(b)
Problem 26
HBr and peroxides are also used to generate 1-bromo-1-alkenes. Suggest a starting reactant that would successfully undergo this reaction.
Problem 27a
Identify the allylic carbon(s) in the following molecules.
(a)
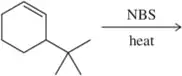
Problem 27b
Identify the allylic carbon(s) in the following molecules.
(b)
Problem 27c
Identify the allylic carbon(s) in the following molecules.
(c)
Problem 28
We show in Chapter 12 that C― Br bonds can break to give a carbocation and a bromide anion. For which of the organohalides (A or B) would you expect this process to be fastest? Explain.
Problem 29
In the following reaction, which C―H bond would be most likely to react with a bromine radical?
Problem 30c
In the following molecules, identify the carbon where the radical is most likely to form in the first propagation step.
(c)
Problem 30d
In the following molecules, identify the carbon where the radical is most likely to form in the first propagation step.
(d)
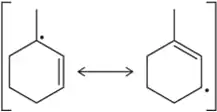
Problem 31a
In the following allylic radicals, identify the carbon where the new C–Br bond is most likely to form in the second propagation step.
(a)
Problem 31b
In the following allylic radicals, identify the carbon where the new C― Br bond is most likely to form in the second propagation step.
(b)
Problem 31c
In the following allylic radicals, identify the carbon where the new C― Br bond is most likely to form in the second propagation step.
(c)
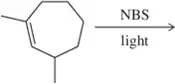
Problem 32a
Predict the products of the following allylic halogenation reactions.
(a)
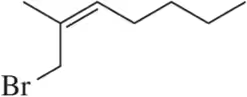
Problem 32c
Predict the products of the following allylic halogenation reactions.
(c)
Problem 32d
Predict the products of the following allylic halogenation reactions.
(d)
Problem 33
The fact that allylic halogenation results in formation of the most stable alkene suggests that it is under thermodynamic control. Thus, the second propagation step must be reversible. Suggest an arrow-pushing mechanism by which the less stable allylic halide might equilibrate to the more stable allylic halide.
Problem 34
(a) Using bond-dissociation energies (Table 5.6), which of the indicated bonds should break most easily?
(b) How does that help you explain the results shown in Figure 11.40?
Problem 35
The following polyunsaturated fat, which does not exist in nature, is oxidized at a rate similar to oleic acid (Table 11.14), despite having two cis-alkenes. Why?
Problem 36
Vitamin E, especially the B ring and the side chain, is a terpenoid derivative. Identify the isoprene units nature used to make it.
Problem 37c
Name the following halogenated compounds according to the IUPAC rules of nomenclature.
(c)
Problem 38a
Draw the structure that corresponds to the compound names shown.
(a) (S)-3-bromo-3-ethylcyclohex-1-ene
Problem 38b
Draw the structure that corresponds to the compound names shown.
(b) (5R,6E)-5-bromooct-6-en-1-yne