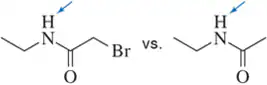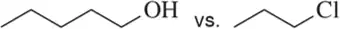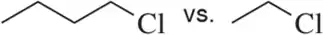Back
Back Mullins 1st Edition
Mullins 1st Edition Ch. 11 - Properties and Synthesis of Alkyl Halides: Radical Reactions
Ch. 11 - Properties and Synthesis of Alkyl Halides: Radical ReactionsProblem 31b
In the following allylic radicals, identify the carbon where the new C― Br bond is most likely to form in the second propagation step.
(b)
Problem 31c
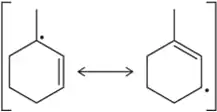
In the following allylic radicals, identify the carbon where the new C― Br bond is most likely to form in the second propagation step.
(c)
Problem 32a
Predict the products of the following allylic halogenation reactions.
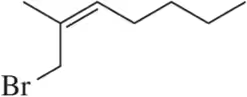
(a)
Problem 32c
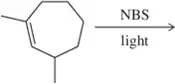
Predict the products of the following allylic halogenation reactions.
(c)
Problem 32d
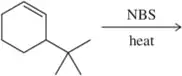
Predict the products of the following allylic halogenation reactions.
(d)
Problem 33
The fact that allylic halogenation results in formation of the most stable alkene suggests that it is under thermodynamic control. Thus, the second propagation step must be reversible. Suggest an arrow-pushing mechanism by which the less stable allylic halide might equilibrate to the more stable allylic halide.
Problem 34
(a) Using bond-dissociation energies (Table 5.6), which of the indicated bonds should break most easily?
(b) How does that help you explain the results shown in Figure 11.40?
Problem 35
The following polyunsaturated fat, which does not exist in nature, is oxidized at a rate similar to oleic acid (Table 11.14), despite having two cis-alkenes. Why?
Problem 36
Vitamin E, especially the B ring and the side chain, is a terpenoid derivative. Identify the isoprene units nature used to make it.
Problem 37c
Name the following halogenated compounds according to the IUPAC rules of nomenclature.
(c)
Problem 38a
Draw the structure that corresponds to the compound names shown.
(a) (S)-3-bromo-3-ethylcyclohex-1-ene
Problem 38b
Draw the structure that corresponds to the compound names shown.
(b) (5R,6E)-5-bromooct-6-en-1-yne
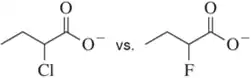
Problem 39b
In each pair, choose the most acidic compound. Justify your answer. The most acidic proton in each compound has been indicated.
(b)
Problem 40d
In each pair, choose the most basic compound. Justify your answer.
(d)
Problem 41a
Which of the reactions studied in this chapter result in oxidation of the organic molecule? Justify your answer.
(a)
Problem 41b
Which of the reactions studied in this chapter result in oxidation of the organic molecule? Justify your answer.
(b)
Problem 41c
Which of the reactions studied in this chapter result in oxidation of the organic molecule? Justify your answer.
(c)
Problem 41d
Which of the reactions studied in this chapter result in oxidation of the organic molecule? Justify your answer.
(d)
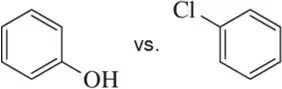
Problem 42(a)
In each pair,
(i) choose the compound that is most soluble in water.
(ii) Within each pair, which is most soluble in nonpolar solvents?
(a)
Problem 42a
In each pair, (i) choose the compound that is most soluble in water. (ii) Within each pair, which is most soluble in nonpolar solvents?
(a)
Problem 42b
In each pair,
(i) choose the compound that is most soluble in water.
(ii) Within each pair, which is most soluble in nonpolar solvents?
(b)
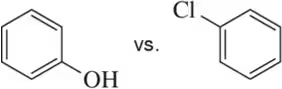
Problem 43a
In each pair, choose the compound you would expect to have the highest boiling/melting point.
(a)
Problem 43b
In each pair, choose the compound you would expect to have the highest boiling/melting point.
(b)
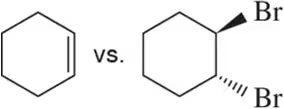
Problem 43c
In each pair, choose the compound you would expect to have the highest boiling/melting point.
(c)
Problem 44
Contrary to expectation, the addition of more fluorines to ethane lowers the boiling point. Explain this phenomenon.
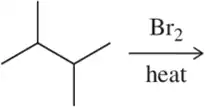
Problem 45b
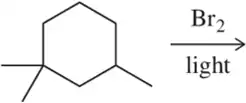
Predict the major product of the following bromination reactions.
(b)
Problem 45c
Predict the major product of the following bromination reactions.
(c)
Problem 46a
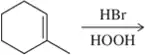
Predict the product of the following alkene addition reactions.
(a)
Problem 46b
Predict the product of the following alkene addition reactions.
(b)
Problem 46c
Predict the product of the following alkene addition reactions.
(c)