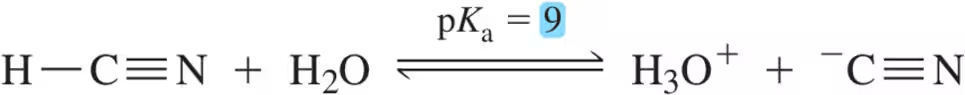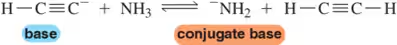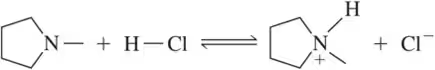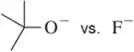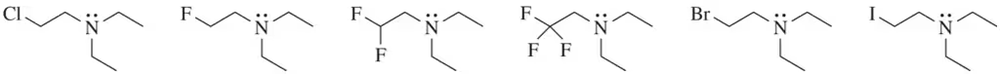Back
BackProblem 30a
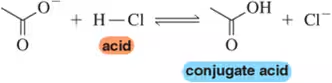
Given that the indicated pKa values correspond to the acid dissociation reactions shown, calculate the ratio of acid to conjugate base for the reactions shown.
(a)
Problem 30b
Given that the indicated pKa values correspond to the acid dissociation reactions shown, calculate the ratio of acid to conjugate base for the reactions shown.
(b)
Problem 31
Hydrogen gas (H2) has a relatively high pKa value. Is it a stable or unstable acid? Do you expect it to participate in acid–base reactions?
Problem 32
How do you know that a proton with a low pKa value is acidic (besides 'I just remember')?
Problem 33
If a base has a conjugate acid with a high pKa value, is it stable or unstable? How do you know this is true (besides 'I just remember')?
Problem 36a
Using qualitative reasoning for the acid–base reactions shown,
(i) which is stronger, the acid or the conjugate acid?
(ii) Which side of the reaction is favored?
(iii) Would you expect a Keq greater than, equal to, or less than 1?
(a)
Problem 36b
Using qualitative reasoning for the acid–base reactions shown,
(i) which is stronger, the acid or the conjugate acid?
(ii) Which side of the reaction is favored?
(iii) Would you expect a Keq greater than, equal to, or less than 1?
(b)
Problem 37a
Using qualitative reasoning for the acid–base reactions shown,
(i) which is stronger, the base or the conjugate base?
(ii) Which side of the reaction is favored?
(iii) Would you expect a Keq greater than or less than 1?
(a)
Problem 37c
Using qualitative reasoning for the acid–base reactions shown,
(i) which is stronger, the base or the conjugate base?
(ii) Which side of the reaction is favored?
(iii) Would you expect a Keq greater than or less than 1?
(c)
Problem 38c
Calculate Keq for these acid–base reactions.
(c)
Problem 38d
Calculate Keq for these acid–base reactions.
(d)
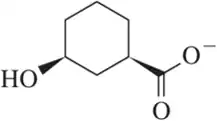
Problem 39b
For each indicated proton, suggest an approximate pKa value from Table 4.5. Rationalize your choice.
(b)
Problem 39d
For each indicated proton, suggest an approximate pKa value from Table 4.5. Rationalize your choice.
(d)
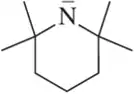
Problem 40b
For the bases shown, draw the conjugate acid and identify a pKa value from Table 4.5 that would help you accurately estimate its stability.
(b)
Problem 40c
For the bases shown, draw the conjugate acid and identify a pKa value from Table 4.5 that would help you accurately estimate its stability.
(c)
Problem 40d
For the bases shown, draw the conjugate acid and identify a pKa value from Table 4.5 that would help you accurately estimate its stability.
(d)
Problem 40e
For the bases shown, draw the conjugate acid and identify a pKa value from Table 4.5 that would help you accurately estimate its stability.
(e)
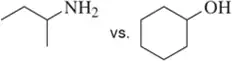
Problem 41a
Without using pKa values, pick out the more acidic compound in each pair. Explain your answer.
(a)
Problem 42a
Without using pKa values, pick out the more reactive (least stable) base in each pair. Explain your answer.
(a)
Problem 44a
Without using pKa values, pick out the least reactive (most stable) base in each pair. Explain your answer.
(a)
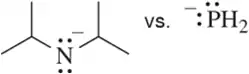
Problem 44b
Without using pKa values, pick out the least reactive (most stable) base in each pair. Explain your answer.
(b)
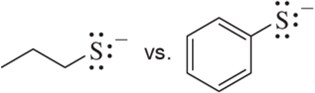
Problem 44c
Without using pKa values, pick out the least reactive (most stable) base in each pair. Explain your answer.
(c)
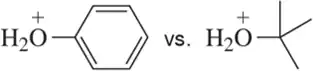
Problem 45a
Which anion in each pair would you expect to react more quickly with H+?
(a)
Problem 45b
Which anion in each pair would you expect to react more quickly with H+?
(b)
Problem 46a
Which acid in each pair would you expect to more readily donate a proton to a basic compound?
(a)
Problem 46b
Which acid in each pair would you expect to more readily donate a proton to a basic compound?
(b)
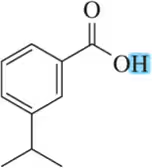
Problem 47
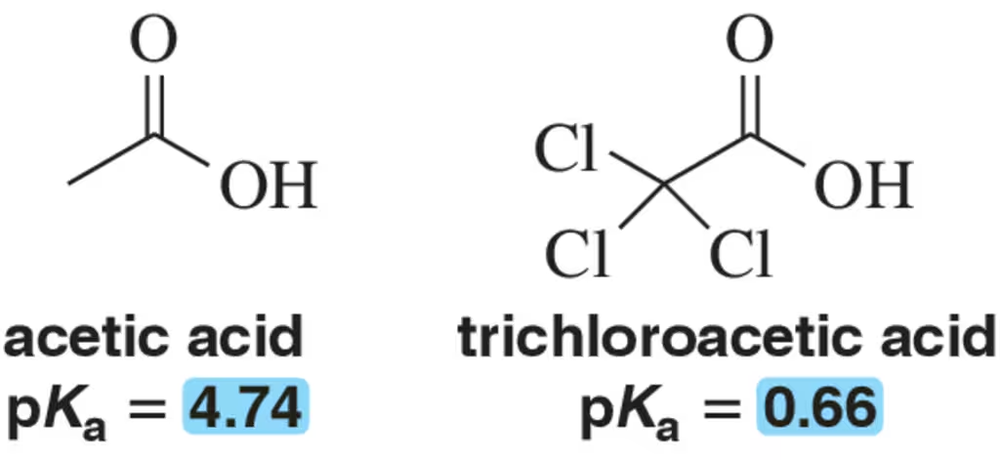
Rationalize the rather large difference in pKa values for the two carboxylic acids shown.
Problem 48
Rank the following alcohols in order of descending pKa value. Explain your ranking.
Problem 49
Rank the following amines in order of their basicity (strongest base = 1 ; weakest base = 6).
Problem 50
If reacted with a strong base, which of the labeled protons would you expect to be removed first?