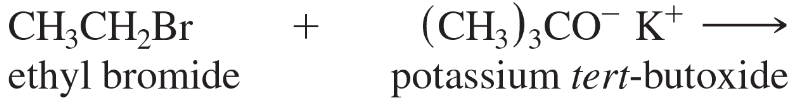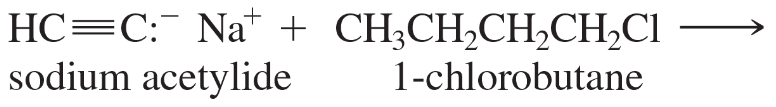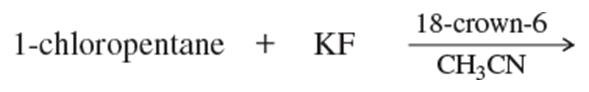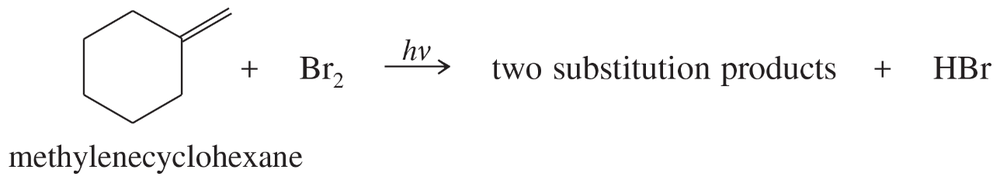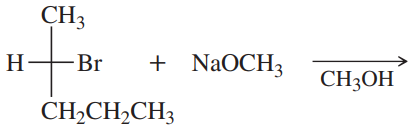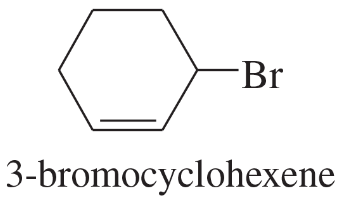Back
BackProblem 13a
Under certain conditions, the reaction of 0.5 M 1-bromobutane with 1.0 M sodium methoxide forms 1-methoxybutane at a rate of 0.05 mol/L per second. What would be the rate if 0.1 M 1-bromobutane and 2.0 M NaOCH3 were used?
Problem 13b
Consider the reaction of 1-bromobutane with a large excess of ammonia (NH3). Draw the reactants, the transition state, and the products. Note that the initial product is the salt of an amine (RNH3+Br−), which is deprotonated by the excess ammonia to give the amine.
Problem 13c
Under certain conditions, the reaction of 0.5 M 1-bromobutane with 1.0 M sodium methoxide forms 1-methoxybutane at a rate of 0.05 mol/L per second.
c. Show another SN2 reaction using a different combination of an alkoxide and an alkyl bromide that also produces 1-methoxybutane.
Problem 14a
Predict the major products of the following substitutions.
a.
Problem 14b
Predict the major products of the following substitutions.
b.
Problem 14d
Predict the major products of the following substitutions.
d. CH3CH2CH2I + NaCN →
Problem 14e
Predict the major products of the following substitutions.
e. 1-chloropentane + NaI →
Problem 14f
Predict the major products of the following substitutions.
f.
Problem 15a
When methylenecyclohexane is treated with a low concentration of bromine under irradiation by a sunlamp, two substitution products are formed.
a. Propose structures for these two products. (b) Propose a mechanism to account for their formation.
Problem 15c,d
Show how you might use SN2 reactions to convert 1-chlorobutane into the following compounds.
c. 1-iodobutane
d. CH3—(CH2)3—CN
Problem 15e,f,g
Show how you might use SN2 reactions to convert 1-chlorobutane into the following compounds.
e. CH3—(CH2)3—C≡CH
f. CH3CH2—O—(CH2)3—CH3
g. CH3—(CH2)3—NH2
Problem 16a,b
For each pair, predict the stronger nucleophile in the SN2 reaction (using an alcohol as the solvent). Explain your prediction.
a. (CH3CH2)3N or (CH3CH2)2NH
b. (CH3)2O or (CH3)2S
Problem 16c,d
For each pair, predict the stronger nucleophile in the SN2 reaction (using an alcohol as the solvent). Explain your prediction.
c. NH3 or PH3
d. CH3S– or H2S
Problem 16e,f
For each pair, predict the stronger nucleophile in the SN2 reaction (using an alcohol as the solvent). Explain your prediction.
e. (CH3)3N or (CH3)2O
f. CH3COO– or CF3COO–
Problem 16g,h
For each pair, predict the stronger nucleophile in the SN2 reaction (using an alcohol as the solvent). Explain your prediction.
g. (CH3)2CHO– or CH3CH2CH2O–
h. I– or Cl–
Problem 17
When diethyl ether (CH3CH2OCH2CH3) is treated with concentrated HBr, the initial products are CH3CH2Br and CH3CH2OH. Propose a mechanism to account for this reaction.
Problem 18
Rank the following compounds in decreasing order of their reactivity toward the SN2 reaction with sodium ethoxide (Na+ –OCH2CH3) in ethanol.
methyl chloride
tert-butyl iodide
neopentyl bromide
isopropyl bromide
methyl iodide
ethyl chloride
Problem 19a,b
For each pair of compounds, state which compound is the better SN2 substrate.
a. 2-methyl-1-iodopropane or tert-butyl iodide.
b. cyclohexyl bromide or 1-bromo-1-methylcyclohexane
Problem 19c,d,e
For each pair of compounds, state which compound is the better SN2 substrate.
c. 2-bromobutane or isopropyl bromide
d. 1-chloro-2,2-dimethylbutane or 2-chlorobutane
e. 1-iodobutane or 2-iodopropane
Problem 20a,b
Draw a perspective structure or a Fischer projection for the products of the following SN2 reactions.
(a) trans-1-bromo-3-methylcyclopentane + KOH
(b) (R)-2-bromopentane + KCN
Problem 20c,d
Draw a perspective structure or a Fischer projection for the products of the following SN2 reactions.
(c)
(d)
Problem 20e
Draw a perspective structure or a Fischer projection for the products of the following SN2 reactions.
(e)
Problem 20f
Draw a perspective structure or a Fischer projection for the products of the following SN2 reactions.
(f)
Problem 22
Propose an SN1 mechanism for the solvolysis of 3-bromo-2,3-dimethylpentane in ethanol.
Problem 23a,b
Choose the member of each pair that will react faster by the SN1 mechanism.
a. 1-bromopropane or 2-bromopropane
b. 2-bromo-2-methylbutane or 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
Problem 23c,d
Choose the member of each pair that will react faster by the SN1 mechanism.
c. n-propyl bromide or allyl bromide
d. 1-bromo-2,2-dimethylpropane or 2-bromopropane
Problem 23e,f
Choose the member of each pair that will react faster by the SN1 mechanism.
e. 2-iodo-2-methylbutane or tert-butyl chloride
f. 2-bromo-2-methylbutane or ethyl iodide
Problem 24a
3-Bromocyclohexene is a secondary halide. It undergoes SN1 substitution about as fast as most tertiary halides. Use resonance structures to explain this enhanced reactivity.
Problem 24b
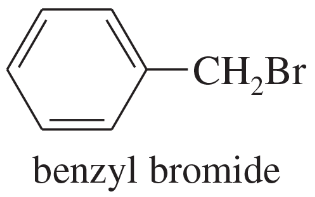
Benzyl bromide is a primary halide. It undergoes SN1 substitution about as fast as most tertiary halides. Use resonance structures to explain this enhanced reactivity.
Problem 25
Give the SN1 mechanism for the formation of 2-ethoxy-3-methylbutane, the unrearranged product in this reaction.